Social Welfare
MGNREGA: Building Rural Resilience
Pillar of Rural Livelihood Security
Posted On:
26 AUG 2025 9:57AM
Key Takeaways
- Rs 86,000 crore allocated for MGNREGA in FY 2025–26 - the highest since the scheme's inception.
- In the Current FY 2025-26, an amount of Rs 45,783 crore has been released under the scheme
- 290.60 crore person-days generated in FY 2024–25.
- With 440.7 lakh women participating in the scheme, participation of women reached to 58.15% by FY 2024–25.
|
Introduction
The Government of India envisions a dignified village life, where the people of Bharat’s rural communities can access growth and opportunity within their own ecosystems. This vision is being realized through the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA), 2005, a flagship programme aimed at enhancing livelihood security by providing at least 100 days of guaranteed wage employment in a financial year to every rural household whose adult members are willing to undertake unskilled manual work.
In Assam, during 2020, farmers faced severe challenges in carrying out agricultural activities due to lack of irrigation water, which significantly affected crop yields. Responding to the needs of the local community, a distributor canal was constructed under the MGNREGA scheme.

The brick-lined canal, built using registered skilled and semi-skilled labour, helped channel rainwater effectively. Upon completion, it provided adequate irrigation to nearby fields, improved livelihoods, and generated a total of 1,134 man-days of local employment.

With a focus on social inclusion, the scheme actively supports SCs, STs, women-headed households, and other vulnerable groups.This scheme emphasizes sustainable development and environmental conservation by encouraging projects that promote ecological restoration and strengthen rural infrastructure. Through initiatives such as water conservation, afforestation, and soil health improvement, MGNREGA is laying the foundation for a greener, more resilient rural India.
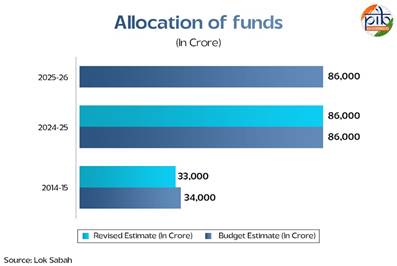
In FY 2013–14, the budget allocation for MGNREGA was Rs 33,000 crore.
On the other hand for FY 2025–26 (BE), the government has retained a high allocation of Rs86,000 crore—the highest since the scheme's inception.
In order to upgrade the skill base of Mahatma Gandhi NREGS workers, the Government of India launched “Project UNNATI” in December 2019. The project aims to enhance the livelihood opportunities of these workers by equipping them with skills that enable a transition from partial employment to full employment, either through self-employment or wage employment. Project UNNATI targets the skill development of 2 lakh MGNREGS workers, thereby promoting sustainable income generation and economic self-reliance.The total achievement till 31st March 2025 was 90,894 candidates.
Key Highlights of Scheme
Objectives under MGNREGA
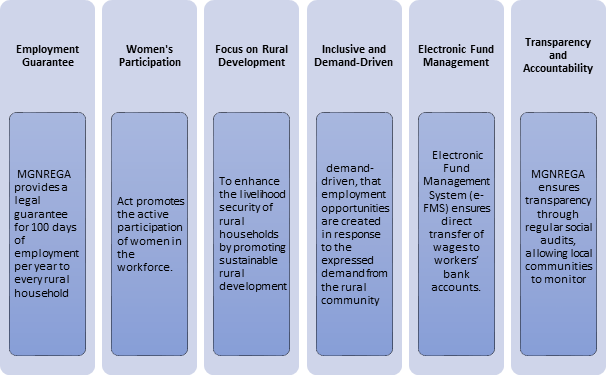
- Providing at least one hundred days of unskilled manual work in a financial year to every household in rural areas as per demand resulting in creation of productive assets of prescribed quality and durability
- Strengthening the livelihood resource base of the poor
- Proactively ensuring social inclusion; and
- Strengthening Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs)
Women Participation under Mahatma Gandhi NREGA
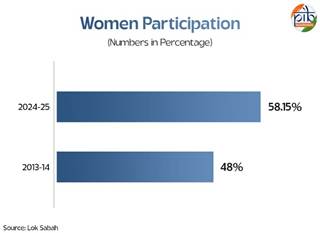
The participation of women under MGNREGA has consistently remained above 50% over the past five financial years. It has shown a steady upward trend, rising from 48% in FY 2013–14 to 58.15% in FY 2024–25 with 440.7 lakh women participating in the scheme during FY 2024–25. This underscores MGNREGA’s critical role in promoting women’s empowerment and economic inclusion in rural areas.
Funds released, Households and Person days Generated under MGNREGS
In the Current FY 2025-26, as on 23.07.2025, an amount of Rs 45,783 crore has been released under the scheme out of which Rs.37,912 crore is for payment of wages.In FY 2024–25, a total of 15.99 crore households were registered under MGNREGA, generating 290.60 crore person-days of employment.
Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS) is a demand-driven wage employment programme that acts as a fallback option when no better employment opportunities are available. The Government of India remains committed to providing adequate employment to all willing and eligible rural households under the scheme as per demand.
During the ongoing financial year 2025–26, 99.79% of rural households that demanded work under MGNREGS were successfully offered employment, reflecting the scheme’s strong responsiveness.
Cancellation of Fake Job cards under MGNEGS
Job card verification is a continuous exercise under the Mahatma Gandhi NREGS, conducted by States and Union Territories using Aadhaar as a tool for de-duplication. Job cards may be cancelled or deleted after proper verification in cases of fake or duplicate entries, households unwilling to work, families that have permanently migrated, or where the sole job cardholder has expired. The number of job cards deleted under MGNREGA in the FY 2024–25 is 58,826.
Comparative Achievement under Mahatma Gandhi NREGA
|
Comparative Achievement under Mahatma Gandhi NREGA
|
|
Sl. No.
|
Financial Year
|
FY 2013-14
|
FY 2024-25 (as on 27.03.25)
|
|
1
|
Women Participation
|
48%
|
58.15%
|
|
2
|
Aadhaar seeding in NREGASoft (Active workers)
|
76 Lakh in Jan, 2014
|
13.45crore
|
|
3
|
Workers on Aadhaar Payment Bridge System (APBS) (Active workers)
|
No such provision
|
13.05 crore
|
|
4
|
Geo-tagging of Mahatma Gandhi NREGS assets
|
No such provision
|
More than 6.26 crore assets already geo-tagged in public domain
|
|
5
|
Status of payment of wages through eFMS (e-Payments)
|
37%
|
99.94%
|
|
6
|
Creation of Individual assets
|
17.6%
|
57.05%
|
Steps undertaken to improve Effectiveness, efficiency, and relevance of MGNREGA
- Mission AmritSarovar: launched in FY 2022 aimed to construct or rejuvenate 50,000 water bodies across India to enhance water conservation. Surpassing its target, over 68,000 AmritSarovars were developed, reflecting a successful “whole of government” approach.
- Social Audit: The social audits of all Gram Panchayats must be conducted at least twice a year to ensure transparency, accountability, and community participation in the scheme's implementation.
- Aadhaar Based Payment System: It has been adopted under the programme to enhance transparency and minimize leakages in wage payments. Through this system, over 99.6% of wage payments are electronically credited directly into workers’ bank accounts, ensuring timely and accountable disbursement of funds.Against the total of 12.08 crore active workers, Aadhaar of 12.03 crore active workers have been seeded so far.
- Secure – Software for Estimate Calculation for using Rural Rates for Employment: Application is being used for estimate the calculation of works to be undertaken under the scheme.
- Yuktdhara portal: It was developed in collaboration with ISRO-NRSC for simplified geospatial planning. It helps integrate local needs with satellite-based data for more effective and targeted development.
- GIS-based planning:It is used as a ridge-to-valley approach which is implemented through remote sensing across all Gram Panchayats.
- JALDOOT App: Enables Gram Rojgar Sahayaks (GRS) to measure and record the water level of selected wells twice a year—pre-monsoon and post-monsoon—to support groundwater monitoring and resource planning.
- JANMANREGA app: aids in proactive disclosure of information to its citizens as well as a feedback mechanism about the implementation of Mahatma Gandhi NREGA.
- National Mobile Monitoring System (NMMS) App: Captures real-time attendance of workers along with geotagged photographs to ensure transparency at worksites.
- GeoMGNREGA: Enables geo-tagging of assets created under the scheme, improving monitoring, planning, and accountability.“During” and “After” stages of the asset creation. So far, a total of 6.36 crore assets has been geotagged.
Recent Developments under MGNREGA
- Around 97.81% of fund transfer orders (FTOs) are being generated on time by the states/UTs ensuring timely wage paymentby March 2025.
- More than 86.98lakh assets have been created by March 2025, reflecting the scheme’s role in strengthening rural infrastructure.
- About 97% of active workers have been linked with Aadhaar Payment Bridge systemby March 2025.
- The Ministry has introduced good governance reforms like job card verification, adoption of 7 simplified registers, stronger social and internal audits, and proactive inclusion of landless labourers. Citizen Information Boards have been deployed to enhance transparency.
- Convergence with 13 Ministries supports infrastructure like Anganwadi centres, GP buildings, and border road connectivity in collaboration with BRO and others.
- Approximatelyby March 2025, 44.14% of total expenditure has been incurred on Agri and allied activities which indicates focus on agriculture in the rural areas.
Measures taken by Central Government to increase awareness
- Launching Information, Education, and Communication (IEC) campaigns, such as wall paintings and community outreach, to widely disseminate the provisions of the Act.
- Expanding the scope and coverage of the demand registration system, ensuring that no genuine demand for work goes unregistered.
- Facilitating participatory planning, with job plans prepared and approved in the Gram Sabha, promoting transparency and local ownership.
- Organizing 'Rozgar Diwas' at the village level to raise awareness about entitlements under MGNREGA, ensure work demand registration, and address grievances.
Conclusion
MGNREGA continues to be a cornerstone of rural employment and development in India. With record budgetary support, increasing women’s participation, and the integration of technology for transparency and accountability, the scheme not only provides livelihoods but also strengthens rural infrastructure and natural resource management. Its evolving framework reflects a strong commitment to inclusive and sustainable rural growth.
Going forward, continuous focus on timely fund flow, effective grievance redressal, and integration with other rural development programs will be crucial to maximize impact. Strengthening social audits, ensuring job card authenticity, and furthering skill development through initiatives like Project UNNATI can enhance both implementation efficiency and long-term livelihood outcomes for rural households.
References
PIB
https://static.pib.gov.in/WriteReadData/specificdocs/documents/2021/nov/doc2021112931.pdf
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2088996#:~:text=Mahatma%20Gandhi%20National%20Rural%20Employment%20Guarantee%20Act%20%28Mahatma,adult%20members%20volunteer%20to%20do%20unskilled%20manual%20work.
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2146875
Lok Sabah Questions
https://sansad.in/getFile/loksabhaquestions/annex/185/AU268_6vAOZG.pdf?source=pqals
https://sansad.in/getFile/loksabhaquestions/annex/185/AU272_LEYckl.pdf?source=pqals
https://sansad.in/getFile/loksabhaquestions/annex/185/AU373_hr66uP.pdf?source=pqals
https://sansad.in/getFile/loksabhaquestions/annex/185/AU1450_vp0m1Z.pdf?source=pqals
https://sansad.in/getFile/loksabhaquestions/annex/185/AS34_WmXz16.pdf?source=pqals
https://sansad.in/getFile/loksabhaquestions/annex/185/AU342_lnThLt.pdf?source=pqals
https://sansad.in/getFile/loksabhaquestions/annex/185/AU306_WYVpgU.pdf?source=pqals
ASSAM Government
https://rural.assam.gov.in/sites/default/files/swf_utility_folder/departments/oc_pnrd_uneecopscloud_com_oid_17/menu/document/march_success_story_assam_0.pdf
Click here to see pdf
****
SK/SM
(Backgrounder ID: 155090)
Visitor Counter : 3183
Provide suggestions / comments