PIB Headquarters
National Social Assistance Programme
“Strengthening India’s Social Security Framework through Inclusive Assistance”
Posted On:
07 NOV 2025 3:31PM by PIB Delhi
 Introduction
Introduction
Introduction
Introduced on 15 August 1995, the National Social Assistance Programme (NSAP) is a fully funded Centrally Sponsored Scheme that extends financial support to individuals living below poverty line (BPL). Implemented by the Ministry of Rural Development, the programme operates across both rural and urban areas, representing a major step towards fulfilling the Directive Principles of State Policy enshrined in the Constitution. NSAP covers old age pension, widow pension, disability pension, family benefit, and food security through Annapurna for those beneficiaries otherwise eligible under Old
Age Pension Scheme but not receiving its benefits.
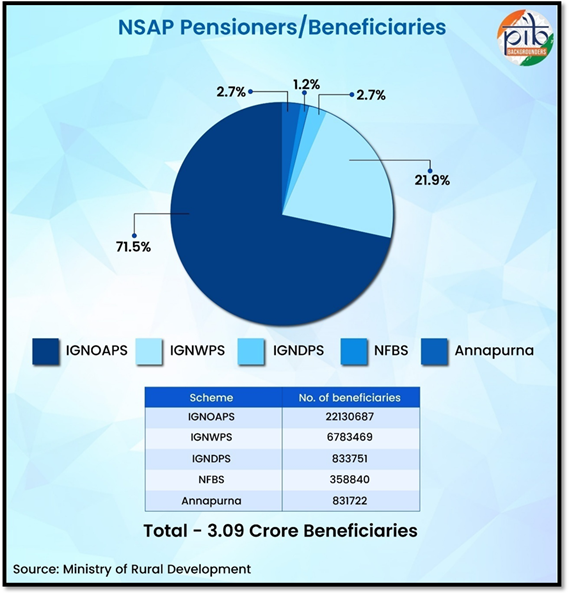
NSAP caters to 3.09 crore beneficiaries with a scheme-wise ceiling/ cap for each State/UT on the number of beneficiaries. This includes 221 lakh elderly persons under the Indira Gandhi National Old Age Pension Scheme (IGNOAPS), 67 lakh beneficiaries under Indira Gandhi National Widow Pension Scheme (IGNWPS), more than 8.33 lakh beneficiaries under Indira Gandhi National Disability Pension Scheme (IGNDPS), 3.5 lakh under National Family Benefit Scheme (NFBS)and 8.31 lakh beneficiaries under Annapurna Scheme, across the country.
Objectives of NSAP
To provide basic level of social security assistance to most vulnerable category of citizens, such as elderly, widow and divyangajan.
Features of Schemes under NSAP
Selection: Gram Panchayats and Municipalities play an active role in identifying eligible beneficiaries under the different NSAP schemes.
Disbursement: Benefits are provided through DBT mode (94%) i.e beneficiary s bank or post office savings accounts, or via postal money orders. Disbursement through Cash at doorstep is also allowed by the scheme guidelines in extreme cases where the beneficiary is unable to go to the bank/post office for receiving the pension.
Monitoring: States and Union Territories have the flexibility to implement the schemes through any State Government department, but each must appoint a Nodal Secretary at the State level to oversee implementation and coordinate with relevant departments. Progress must be reported quarterly in a prescribed format by the 15th day of the month following each quarter. Non-submission of progress reports is considered a lack of progress and may result in non-release of additional central assistance for the final quarter of the financial year.
Components of NSAP
The NSAP at present comprises five sub-schemes as its components -
Indira Gandhi National Old Age Pension Scheme (IGNOAPS)
Indira Gandhi National Widow Pension Scheme (IGNWPS)
Indira Gandhi National Disability Pension Scheme (IGNDPS)
National Family Benefit Scheme (NFBS)
Annapurna Scheme
Indira Gandhi National Old Age Pension Scheme (IGNOAPS)
The Indira Gandhi National Old Age Pension Scheme extends financial assistance to elderly citizens aged 60 years and above who belong to families living below the poverty line by the Government of India. Under this scheme, individuals between 60 and 79 years of age receive Rs.200 per month from the Central Government, while those aged 80 years and above are provided Rs.500 per month.
In accordance with the guidelines of the National Social Assistance Programme, States and Union Territories are encouraged to supplement the Central share by contributing an equivalent or higher top-up amount. This additional support helps ensure that the beneficiaries receive a reasonable and dignified level of income. Currently, the top-up provided by States and UTs under the old age pension component ranges from Rs.50 to Rs. 5700 per month, leading to an average pension of around Rs.1100 in many of the States/UTs.

Indira Gandhi National Widow Pension Scheme (IGNWPS)
Under this scheme, financial assistance is extended to widows aged between 40 and 79years who belong to families living below the poverty line, as identified by the Government of India. Each eligible beneficiary in this age group receives Rs.300 per month as central assistance. For widows who are 80 years and above, the amount of central assistance is Rs.500 per month, providing essential financial support to help meet their basic needs.
Indira Gandhi National Disability Pension Scheme (IGNDPS)
With a total of Rs.243.74 crore released to States and Union Territories under the Indira Gandhi National Disability Pension Scheme (IGNDPS) for the year 2024 25, this scheme caters individuals aged between 18 and 79 years who have severe or multiple disabilities and belong to families living below the poverty line. The beneficiaries are eligible for central assistance of Rs.300 per month. Beneficiaries who are 80 years and above receive Rs.500 per month, ensuring continued financial support to help them manage their daily needs with dignity.
National Family Benefit Scheme (NFBS)
Under this scheme, a household living below the poverty line becomes eligible for lump sum financial assistance in the unfortunate event of the death of its primary breadwinner, provided the deceased was between 18 and 59 years of age. The family receives Rs.20,000 as support to help them cope with the immediate financial difficulties arising from the loss.
Annapurna Scheme
Under the scheme, 10kg of food grains per month are provided free of cost to those senior citizens who, though eligible under Indira Gandhi National Old Age Pension Scheme (IGNOAPS), are not receiving old age pension.
Budgetary Allocation
The budget allocation for the National Social Assistance Programme for the year 2025 26 stands at Rs.9,652 crore.
Budget allocated under Components of NSAP for the year 2025-26:
|
S.no.
|
Component
|
Budget 2025-26 (In Rs. crore)
|
|
1.
|
Indira Gandhi National Old Age Pension Scheme (IGNOAPS)
|
6645.90
|
|
2.
|
Indira Gandhi National Widow Pension Scheme (IGNWPS)
|
2026.99
|
|
3.
|
National Family Benefit Scheme
|
659.00
|
|
4.
|
Indira Gandhi National Disability Pension Scheme (IGNDPS)
|
290.00
|
|
5.
|
Annapurna Scheme
|
10.00
|
|
6.
|
Management Cell
|
20.11
|
|
|
Total
|
9652.00
|
Digitization of Beneficiaries
The details of all potential beneficiaries have now been fully digitised, including their names, addresses, choice of pension disbursement mode, bank account information, Aadhaar numbers, and mobile numbers wherever available.
So far, under NSAP, a total of more than 2.5 crore beneficiaries have their Aadhaar numbers linked to their account ensuring secure and direct transfer of benefits. This information is accessible to the public on the official NSAP portal at www.nsap.nic.in
The digital initiative has ensured that pensions are credited directly into the bank accounts of eligible beneficiaries, with Aadhaar authentication and Public Financial Management System (PFMS) integration helping to eliminate bogus entries and promote transparency.
Aadhaar based Mobile Application for Digital Life Certification (DLC) of NSAP pension beneficiaries has been launched by Hon ble Minister of Rural Development on 15th July, 2025. The DLC application will ease the process of annual life verification of beneficiaries which was hitherto carried out manually by the States/UTs.
Conclusion
The National Social Assistance Programme serves as a key pillar of India s social security system, providing essential support to citizens in need. Through its various components- the Indira Gandhi National Old Age Pension Scheme, the Indira Gandhi National Widow Pension Scheme, the Indira Gandhi National Disability Pension Scheme, Annapurna Scheme and the National Family Benefit Scheme, the programme ensures that elderly citizens, widows, persons with disabilities, and families experiencing the loss of a primary breadwinner receive regular financial assistance and food security. By integrating Aadhaar-based authentication and promoting direct benefit transfers, NSAP has improved transparency, reduced fraud, and strengthened the delivery of welfare to millions of beneficiaries. Collectively, these measures offer critical financial relief and contribute to a more inclusive and equitable social safety net across the country.
References
Ministry of Rural Development
https://www.dord.gov.in/static/uploads/2024/02/43f6d3ecbd0cf21b1a0c23d80d270e0c.pdf
National Social Assistance Programme
https://nsap.nic.in/
https://nsap.nic.in/circular.do?method=faq#collapse3
https://nsap.nic.in/circular.do?method=faq#collapse12
Manipur State National Informatics Centre
https://manipur.nic.in/news/manipur-awarded-for-100-dbt-for-nsap-by-ministry-of-rural-development/
My Scheme Portal
https://www.myscheme.gov.in/schemes/nsap-ignoaps
Rajya Sabha
https://sansad.in/getFile/annex/268/AU2384_qLzV6d.pdf?source=pqars
https://sansad.in/getFile/loksabhaquestions/annex/185/AU3825_81y9WL.pdf?source=pqals
https://sansad.in/getFile/loksabhaquestions/annex/185/AU3882_9TjvAE.pdf?source=pqals
https://sansad.in/getFile/annex/268/AU2384_qLzV6d.pdf?source=pqars
India Budget
https://www.indiabudget.gov.in/doc/eb/sbe87.pdf
PIB Press Release
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2152593
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2088996&utm_source
Click here to see PDF
********
SK/SM
(Release ID: 2187327)
Visitor Counter : 5336