PIB Headquarters
Handicrafts at the Heart of India’s Rural Economy
Posted On:
09 DEC 2025 3:51PM by PIB Delhi

Introduction

India’s handicraft sector plays a vital role in the country’s economy, especially in rural areas. It provides livelihoods to a large number of artisans and craftspersons across rural and semi-urban regions, contributes to exports, and helps preserve India’s rich cultural heritage.With 318 GI-tagged handicraft products and around 455 formally classified craft categories, the sector reflects the remarkable diversity of India’s creative traditions.
|
The Art Behind Every Handicraft
Handicrafts are goods predominantly made by hand even though some tools or machinery may also have been used in the process; such goods are graced with visual appeal; possess distinctive features, which can be aesthetic, artistic, ethnic or culturally attached and are amply different from mechanically produced goods of similar utility.
|
India is one of the world’s important suppliers of handicrafts; and with growing global demand for authentic, sustainable handmade products, the country is uniquely positioned to scale up its handicraft economy. A vast number of artisans across the Indian states, possess inherent skills, techniques and traditional craftsmanship, forming the backbone of the Handicrafts Industry. Even though a majority of the artisans engage in crafts work on a part-time bases with low capital investment, the value addition remains high making handicrafts a viable source of income. The sector is highly labour- intensive and decentralized, spread across the length and breadth of the country.
|
Celebrating India’s Craft Heritage
National Handicrafts Week (December 8-14) is observed annually to celebrate India’s artisans and highlight the cultural and economic significance of the handicraft sector. It provides an opportunity to recognize the contribution of craft communities, promote traditional skills, and reinforce the Government’s commitment to strengthening this vital segment of the rural economy.
Recognizing Excellence in Craftsmanship
A key feature this year is the National Handicrafts Awards, which recognize exceptional master crafts persons for their outstanding contributions to India’s craft heritage. These include the Shilp Guru Awards, the highest honour in the handicrafts sector, and the National Awards, which acknowledge excellence and innovation across diverse craft forms. Together, these awards celebrate the skill, creativity, and cultural stewardship of artisans across the country.
|
Economic Strength of the Handicraft Sector
Employment and Artisan Demographics
The handicrafts industry employs a large number of artisans, particularly from rural areas. India currently has an estimated 64.66 lakh handloom and handicraft artisans, with a significant share concentrated in states such as Uttar Pradesh, Rajasthan, Assam, Odisha, West Bengal and Tamil Nadu. As of August 2025, women accounted for71% of the handloom weavers and 64% of total artisans. Such a strong participation of women underscores the sector’s role in supporting women’s employment and empowerment in rural and semi-urban communities.
The sector plays an important role in uplifting the social stature of the economy, with a diverse artisans’ workforce- majority belonging to Scheduled Castes (SCs), Scheduled Tribes (STs) and Other Backward Classes (OBCs). This reflects a broad-based involvement of various communities in craft activities, making the handicraft sector a vehicle for inclusive growth and livelihood across different sections of society.
The Indian Handicrafts Sectoralso provides part-time or supplemental employment to agrarian households and others, helping ensuresmooth income flowsduring off-seasonsandperiods of insufficient agricultural work. Moreover, since crafts can be practiced with small setups (often home-based) and with minimal capital, they offer a viable source of livelihood, especially tohouseholds in remote areas.
|
As of 2024, the Pehchan Artisan Identification programme has registered over 32 lakh artisans. Nearly 20 lakhs of these artisans are women, highlighting the scheme’s role in empowering rural women economically.
|
The Government recognizes handicrafts as a key source of livelihood, aiding in strengthening local non-farm employment. Many traditional craft skills are passed down through generations andwith institutional support, these skills are being recognised and promoted. The Government’s initiative to issue Pehchan ID cards to artisans is aimed at bringing these artisans into the formal economy, enabling them to avail benefits under the Government of India Schemes.By formalizing artisan identities and organizing them, the groundwork is being laid for better working conditions and bargaining power for craft workers.
In the first half of FY2025 (April-September 2025), India’s total textiles & apparel (including handicrafts) exports stood at US$ 18,235.44 million.India’s handicraft exports have grown impressively, as also witnessed by stable performance of total textiles & apparel sector despite the global challenges. In the year 2024-25, the export of handicrafts (excluding hand-knotted carpets) reached ₹33,122.79 crore, up from ₹20,082.53 crore in 2014-15 .
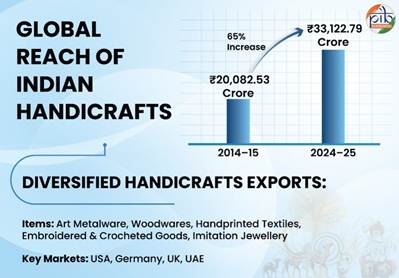
Key categories of exportsduring the year 2024-25 include art metal wares (₹4,386 crore), woodwares (₹8,524 crore), handprinted textiles (₹3,217 crore), embroidered and crocheted goods (₹4,350 crore), and imitation jewellery (₹1,511 crore) among others. These numbers reflect the range of India’s craft exports and demonstratethe global appetite for Indian craft products. With around 37%, USA remains a major buyer, while61% of India’s handicrafts are destined for other major markets.
With India’s robust economic growth and the government actively assisting exporters, the outlook for handicraft exports remains positive.
Empowering Craftsmanship: Government Support for Handicrafts
The Government has demonstrated support for the handloom and handicrafts sector through a slate of dedicated schemes and policy interventions. This consistent support has been crucial in modernizing the sector, enhancing artisans’ incomes, and ensuring the sector’s resilience. Key government initiatives and their impacts include:
National Handicraft Development Programme (NHDP):
NHDP is the flagship scheme for handicraft sector promotion. It has an approved outlay of ₹837 crore for FY2022-26. During 2023-24, 2,325 projects and events were sanctioned under NHDP, benefiting 66,000+ artisans.
The scheme provides comprehensive support to handicraft clusters and artisans through basic inputs, infrastructure support, and capacity enhancement to cater to target markets. Its components are designed to offer end-to-end assistance, create a conducive environment, and ensure fair competition with machine-made products.
The focus is to bring every artisan into the mainstream while preserving traditional crafts by offering marketing platforms, infrastructure support, and design and skill training for new entrants. Along with strengthening the sector and empowering artisans, the scheme also extends social security through initiatives like Aam Admi Jeevan Jyoti Yojana and Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Yojana, including pension support for elderly artisans.
In essence, NHDP scheme adopts the following three-pronged approach to put the sector on high growth trajectory as well as preserving existing cultural heritage: -
- Promoting premium handicraft products for the niche market.
- Expansion of production base for utility-based, life style and mass production handicrafts products.
- Empowerment and sustainability of artisans along with preservation and protection of heritage/ languishing crafts.
|
Empowering Artisans Through Structured Skill Development Initiatives
Today, standardized production, skilled manpower, design databases, quick & efficient prototyping, and better communication skills are essential to match the evolving production and distribution of crafts to both national and global markets.With advancements in tools & technology, the artisan’ workforce in India is evolving rapidly. To support artisans in these areas, “Skill Development in Handicraft Sector”under the NHDP has been conceptualized to fulfil these requirements and has the following four components:
- Design and Technology Development Workshop: Focuses on meeting current market design needs by developing new designs and prototypes using the existing skills of artisans.
- Guru Shishya HastshilpPrashikshan Program: Aims to transfer traditional craft knowledge from master crafts persons to new artisans through technical and soft-skill training, helping bridge the skill gap and create a trained workforce for market needs.
- Comprehensive Skill Upgradation Program: Bridges skill gaps by reviving traditional crafts through National Skills Qualifications Framework (NSQF) training, enabling skill upgradation, design innovation and artisan skills.
- Improved Toolkit Distribution Program:Provides improved toolkits to artisans to enhance productivity, ensure uniform quality, and support larger-scale production in the handicraft sector.
|
Sector Promotion Through Artisan Clusters
- Comprehensive Handicrafts Cluster Development Scheme (CHCDS)
Complementing NHDP is the Comprehensive Handicrafts Cluster Development Scheme (CHCDS) with an outlay of ₹142.5 crore for FY2022-26. The objective of the program is to develop handicraft clusters with world-class infrastructure to meet the business needs of local artisans and Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs), enabling higher production and export.
The clusters aim to support artisans and entrepreneurs in establishing modern units equipped with advanced infrastructure, updated technology, and adequate training and human resource development inputs, along with market linkages and production diversification.
The broad objectives of the program are as follows:
- To enhance the competitiveness of selected clusters by increasing market share and productivity through higher unit value realization.
- To integrate scattered artisans, strengthen grassroots enterprises, and link them with SMEsto achieve economies of scale, build critical mass, and meet global market requirements of quality and standardization.
- To provide essential support and linkages in infrastructure, technology, product diversification, design development, raw material banks, marketing, promotion, and social security to ensure long-term sustainability.
- The strategy includes strong technical and program management assistance for capacity building, designing interventions, and implementing them through a competent professional agency.

- Scheme of Fund for Regeneration of Traditional Industries (SFURTI)
India’s handicraft sector is closely linked to the country’s rural development efforts and supports non-farm livelihoods. There are over 100 handicraft clusters under the Scheme of Fund for Regeneration of Traditional Industries (SFURTI), which aim to recognize the talent, creativity, enterprise and hard work of rural artisans in a variety of fields, and to make traditional industries more productive, profitable and capable of generating sustained employment, subsequently empowering and converting artisans into self-governing entrepreneurs.
|
Self-Reliant Artisans
Under schemes like the Ambedkar Hastshilp Vikas Yojana (component of National Handicrafts Development Programme), the Government supports the formation of artisan collectives or producer companies in these clusters and provides them need-based interventions like design & technical development workshop etc.
The aim is to integrate artisans into the financial and marketing mainstream while preserving their traditional crafts.
|
Market Access, and Global Integration
The handicraft sector’s support to rural development is further evidenced by its inclusion in various government programs. For instance, by supporting GI tagged products that keep traditional skills alive, the One District One Product (ODOP) initiative highlights regional products of many districts, thereby supporting development. Many Self-Help Groups (SHGs) engage in artisanal production, supported by capacity-building and eco-friendly innovations. In order to connect rural artisans with urban marketplaces that also offer global integration, the Government facilitates marketing events and exhibitions.
In FY 2023-24 alone, 786 domestic and international marketing events were sanctioned under National Handicraft Development Programme, alongside design and training initiatives, benefitting around 66,775 artisans across India. In 2025-26, a total of 132 marketing events have been planned under NHDP. These events are designed to strengthen market access for artisans.
|
Platforms Enhancing Visibility & Opening New Market Linkages
Indie Haat – Showcasing India’s Handicraft and Handloom Heritage: The 2025 edition of Indie Haat, held from 12th to 18th February 2025 at the National Crafts Museum &Hastkala Academy, New Delhi, featured a vibrant display of 80 different types of handcrafted and handwoven products, created by 85 artisans and weavers from across the country.
Special Handloom and Handicraft Exhibition at IITF: As part of the India International Trade Fair (IITF) at Bharat Mandapam, the Ministry of Textiles organized a Special Handloom and Handicraft Exhibition cum Sale, curated by the Office of the Development Commissioner for Handlooms and Handicrafts. The Pavilion showcased 206 stalls representing handloom and handicraft traditions from 27 states, along with a thematic display on “Tribal Treasures of Indian Textiles.”
|
Handloom Sector Initiatives
Given the close kinship between handlooms and handicrafts, the Government sanctioned 356 Small and 2 Mega Handloom clusters, organised 880 Marketing events, sanctioned 42,895 MUDRA Loans, enrolled 5,34,162 weavers under Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana (PMJJBY)/ Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojana (PMSBY) and formed 163 Producer Companies(as on 02.12.2025) to benefit Handloom weavers across the country during the last 5 years. These benefits have reached nearly 6.45 lakh handloom wavers across the country.
Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme for MSME Participation: Further, to enhance MSME participation, the Government has amended the scheme by reducing the investment requirement for new applicants. The investment requirement is reduced from Rs.300 crore to Rs.150 crore (Part-1) and Rs.100 crore to Rs.50 crore (Part-2). The minimum incremental turnover criteria have also been reduced from 25% to 10% and the product basket has been expanded to include more man-made fibre (MMF) apparel, fabrics, and technical textiles. The requirement of setting up a new company for availing the benefit of the Scheme has also been removed.
Skill Development Support: Alongside production incentives, schemes like SAMARTH – Scheme for Capacity Building in Textile Sector have been extended to train artisans and weavers. Under Samarth, 5.35 lakh beneficiaries were trained and 4.20 lakh provided job placements as of December 2025.
Market Promotion and Infrastructure: To promote textile and handicraft trade both nationally and internationally, the Ministry facilitates Export Promotion Councils (EPCs), including traditional product–focused councils such as the Handloom Export Promotion Council (HHEC), Carpet Export Promotion Council (CEPC), and the Export Promotion Council for Handicrafts (EPCH), as well as industry associations, for participation in trade fairs and expos. The Ministry also supports the Global Mega Textile Event, Bharat TEX, which showcases the strength of India’s textiles value chain and highlights the latest innovations in the textile, fashion, and handicraft sectors, positioning India as a preferred global destination for sourcing and investment.
Export Promotion Initiatives: India’s exports of Textile & Apparel, including handicrafts, demonstrated remarkable resilience in the first half of FY 2025-26 despite global headwinds. To promote the sector’s exports (including handicrafts) globally and improve its export competitiveness, the Government implemented Rebate of State and Central Taxes and Levies (RoSCTL) scheme. Textile products not covered under RoSCTL (implemented for apparel/garments and made-ups) are covered under the scheme - Remission of Duties and Taxes on Exported Products (RoDTEP), that will reduce hidden export costs (taxes & duties). Additionally, since MSMEs largely contribute to production of handicrafts, the recent Export Promotion Mission, through its two components NiryatProtsahan (focusing on financial enablers) and Niryat Disha (focusing on non-financial enablers), is expected to contribute in the overall production, delivery and growth of the handicrafts sector.
The most recent policy reforms include GST Rationalisation and Integration of 29 labour laws into 4 labour codes viz. the Code on Wages 2019, the Code on Social Security 2020, the Code on Industrial Relations 2020 and the Code on Occupational, Safety, Health and Working Conditions 2020. GST rate cuts on idols, paintings, inlay work, terracotta, handbags, artware, tableware have brought a huge relief for artisans and crafts people. This encourages indigenous production under Vocal for Local, reduces dependence on import and, creates jobs. The codes together support worker welfare and dignity. Provisions like Universalisation of Minimum Wages, Prohibition of Gender Discrimination and Extended Social Security will benefit all workers.
Conclusion
India’s handicraft sector plays a crucial role in the country’s economy and cultural identity. By supporting millions of artisans across rural and semi-urban areas, it reflects India’s deep reservoir of traditional skills and craftsmanship. With growing global interest in handmade and sustainable products, the sector has strong potential for expansion.Government initiatives & schemes, covering skill training, cluster development, marketing support, digital platforms, and export facilitation, are aimed at creating better opportunities for artisans and helping them access wider markets. These interventions are improving productivity, strengthening value chains, and enabling artisans to earn more predictable and higher incomes.
With an enriching combination of rich heritage, skilled artisans, and consistent policy support, India’s handicraft sector is well-placed to drive inclusive growth, support rural livelihoods, and contribute meaningfully to India’s economic progress in the coming years.
PIB Research
References
DC-MSME (Handicrafts):
About Us | Official website of Development Commissioner (Handicrafts), Ministry of Textiles, Government of India
https://handicrafts.nic.in/pdf/GIList.pdf
https://handicrafts.nic.in/pdf/NewCraft.pdf
handicrafts.nic.in/CraftDefinition.aspx
https://handicrafts.nic.in/pdf/Scheme.pdf
https://indian.handicrafts.gov.in/static-pdf/scheme-guideline.pdf
https://handlooms.nic.in/assets/img/upcoming_markeing/AMC2025-26_02-04-2025.pdf
M/o MSME:
sfurti.msme.gov.in/SFURTI/Reports/DPR_Functional_Upto.aspx
https://www.msme.gov.in/sites/default/files/MSME-ANNUAL-REPORT-2024-25-ENGLISH.pdf
https://static.pib.gov.in/WriteReadData/specificdocs/documents/2022/apr/doc20224636101.pdf
M/o Textiles:
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2199236®=1&lang=1
https://www.pib.gov.in/Pressreleaseshare.aspx?PRID=2089306®=3&lang=2
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2197522®=3&lang=1
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2157864®=3&lang=2#:~:text=Govt,reliant
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2073886®=3&lang=2
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2197519®=3&lang=2
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2199515®=3&lang=1
M/o Finance:
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2192229®=3&lang=2
https://www.pib.gov.in/FactsheetDetails.aspx?Id=149281®=3&lang=1
M/o Labour & Employment:
https://www.pib.gov.in/FactsheetDetails.aspx?Id=150508®=3&lang=1
Export Promotion Council for Handicrafts:
https://www.epch.in/sites/default/files/policies/exportsofhandicrafts.htm
Parliamentary Responses:
https://sansad.in/getFile/loksabhaquestions/annex/185/AS237_eb5QqY.pdf?source=pqals
https://sansad.in/getFile/loksabhaquestions/annex/185/AU351_GpRWNL.pdf?source=pqals
https://sansad.in/getFile/loksabhaquestions/annex/184/AU4956_YS5OfB.pdf?source=pqals
Others:
https://ddnews.gov.in/en/president-murmu-to-confer-handicrafts-awards-on-december-9/
https://www.ibef.org/blogs/empowering-districts-empowering-india-the-odop-revolution
Click here for pdf file.
****
PIB Research
(Release ID: 2200859)
Visitor Counter : 5681