Ministry of Railways
Railway Safety at Record High: Annual Accidents Reduce from 171 (2004–14 Avg.) to 11 in 2025–26 So Far
Safety Budget Grows Almost Three Times From ₹39,463 Crore in 2013–14 to ₹1,16,470 Crore in Current Fiscal
Fog Safety Devices Rise 288 Times — From 90 in 2014 to 25,939 in 2025: Ashwini Vaishnaw
Centralised Electronic Interlocking and Track-Circuiting Completed in 21 Stations Each Over the Last Four Months
Posted On:
12 DEC 2025 2:01PM by PIB Delhi
Safety and Security of passengers is accorded high priority on Indian Railways. Any unusual incident is thoroughly investigated by the Railway Administration. Wherever any reason other than technical reason is suspected, the help of State Police is taken.
In some cases, the guidance of Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) and National Investigation Agency (NIA) is also sought. However, the primary means of investigation is through the State Police. This is in line with the constitutional arrangements under which the investigation of criminal activity, maintenance of Law and Order and security of railway infrastructure i.e. tracks, bridges, tunnels etc. is responsibility of the State Government.
In all incidents of sabotage/tampering with railway track reported in 2023 and 2024, cases have been registered by Police/GRP of states and other law enforcement agencies followed by investigation, arrest of offenders and their prosecution.
The following steps are being taken by Railways for better coordination with State Police/GRP, for coordinated action to prevent such incidents and its monitoring :-
- Frequent patrolling of identified black spots and vulnerable sections are being jointly done by Railwaymen, RPF, GRP & Civil Police.
- Special teams are formed to patrol high-risk areas, vulnerable sections and sharing of intelligence to mitigate threats effectively.
- Regular drives are conducted to remove material lying near to the railway tracks which can potentially be used by miscreants for obstruction by putting those materials on railway track.
- The people living near railway track are being sensitized about the consequences of putting foreign material on track, removing rail components etc. and are requested to keep watch and report any suspected activity immediately.
- State Level Security Committee of Railways (SLSCR) meetings are being conducted, which have been constituted in each State under the chairmanship of DGsP/Commissioner of Police of respective States/Union territory with representatives of RPF, GRP and Intelligence units. Close liaison is actively made by RPF with the State Police/GRP authorities at all levels to control Crime, registration of cases, their investigation and maintenance of Law & Order in Railway premises as well as on running trains with focus on sabotage incidents, sharing of intelligence. Effective steps are being undertaken to prevent such incidents. In addition to above, specialized agencies such as NIA, CBI are also involved as per the scenario.
- Besides Central & State Intelligence agencies, Intelligence unit of RPF i.e. CIB & SIB regularly sensitized and instructed to collect intelligence and take necessary action in coordination with Police authorities for detection and prevention of sabotage attempts.
To improve Safety in train operations, several measures have been taken by Indian Railways. As a consequence of various safety measures taken over the years, there has been a steep decline in the number of accidents. Consequential Train Accidents have reduced from 135 in 2014-15 to 31 in 2024-25 as shown in the graph below.
It may be noted that the Consequential Train Accidents during the period 2004-14 was 1711 (average 171 per annum), which has declined to 31 in 2024-25 and further to 11 in 2025-26 (upto November, 2025).
The number of consequential train accidents during the last five years is depicted in the graph below:-
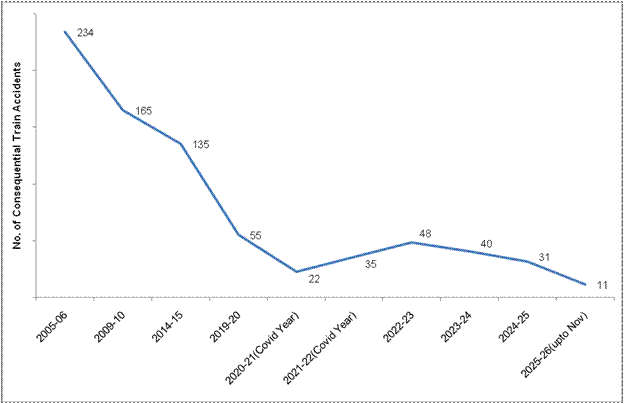
The various safety measures taken to enhance safety in train operations are as under:-
- On Indian Railways, the expenditure on Safety related activities has increased over the years as under:-
|
Expenditure/Budget on Safety related activities (Rs. in Cr.)
|
|
2013-14 (Act.)
|
2022-23 (Act.)
|
2023-24 (Act.)
|
2024-25
|
2025-26
|
|
39,463
|
87,327
|
1,01,651
|
1,14,022
|
1,16,470
|
- Electrical/Electronic Interlocking Systems with centralized operation of points and signals have been provided at 6,656 stations up to 31.10.2025 to reduce accident due to human failure.
- Interlocking of Level Crossing (LC) Gates has been provided at 10,098 Level Crossing Gates up to 31.10.2025 for enhancing safety at LC Gates.
- Complete Track Circuiting of stations to enhance safety by verification of track occupancy by electrical means has been provided at 6,661 stations up to 31.10.2025.
- Kavach is a highly technology intensive system, which requires safety certification of highest order. Kavach was adopted as a National ATP system in July 2020. Kavach is provided progressively in phased manner. Initially, Kavach Version 3.2 was deployed on 1465 RKm of South Central Railway and 80 RKm of North Central Railway. Kavach specification Version 4.0 was approved by RDSO on 16.07.2024. After extensive and elaborate trials, Kavach Version 4.0has been successfully commissioned on Palwal-Mathura-Kota- Nagda section (633Rkm) on Delhi- Mumbai route and on Howrah-Bardhaman section ( 105RKm)on Delhi-Howrah route. Kavach implementation has been taken up in balance sections of Delhi-Mumbai and Delhi-Howrah route. Further, Kavach implementation has been taken up on 15,512 RKm covering all GQ, GD, HDN and identified sections of Indian Railways.
- Detailed instructions on issues related with safety of Signalling, e.g. mandatory correspondence check, alteration work protocol, preparation of completion drawing, etc. have been issued.
- System of disconnection and reconnection for S&T equipment as per protocol has been re-emphasized.
- All locomotives are equipped with Vigilance Control Devices (VCD) to improve alertness of Loco Pilots.
- Retro-reflective sigma boards are provided on the mast which is located two OHE masts prior to the signals in electrified territories to alert the crew about the signal ahead when visibility is low due to foggy weather.
- A GPS based Fog Safety Device (FSD) is provided to loco pilots in fog affected areas which enables loco pilots to know the distance of the approaching landmarks like signals, level crossing gates, etc.
- Modern track structure consisting of 60kg, 90 Ultimate Tensile Strength (UTS) rails, Prestressed Concrete Sleeper (PSC) Normal/Wide base sleepers with elastic fastening, fan shaped layout turnout on PSC sleepers, Steel Channel/H-beam Sleepers on girder bridges is used while carrying out primary track renewals.
- Mechanisation of track laying activity through use of track machines like PQRS, TRT, T-28 etc. to reduce human errors.
- Maximizing supply of 130m/260m long rail panels for increasing progress of rail renewal and avoiding welding of joints, thereby improving safety.
- Ultrasonic Flaw Detection (USFD) testing of rails to detect flaws and timely removal of defective rails.
- Laying of longer rails, minimizing the use of Alumino Thermic Welding and adoption of better welding technology for rails i.e., Flash Butt Welding.
- Monitoring of track geometry by OMS (Oscillation Monitoring System) and TRC (Track Recording Cars).
- Patrolling of railway tracks to look out for weld/rail fractures.
- The use of Thick Web Switches and Weldable CMS Crossing in turnout renewal works.
- Inspections at regular intervals are carried out to monitor and educate staff for observance of safe practices.
- Web based online monitoring system of track assets viz. Track database and decision support system has been adopted to decide rationalized maintenance requirement and optimize inputs.
- Detailed instructions on issues related with safety of Track, e.g. integrated block, corridor block, worksite safety, monsoon precautions, etc. have been issued.
- Preventive maintenance of railway assets (Coaches & Wagons) is undertaken to ensure safe train operations.
- Replacement of conventional ICF design coaches with LHB design coaches is being done.
- All unmanned level crossings (UMLCs) on Broad Gauge (BG) route have been eliminated by January 2019.
- Safety of Railway Bridges is ensured through regular inspection of Bridges. The requirement of repair/rehabilitation of Bridges is taken up based upon the conditions assessed during these inspections.
- Indian Railways has displayed Statutory “Fire Notices” for widespread passenger information in all coaches. Fire posters are provided in every coach so as toeducate and alert passengers regarding various Do’s and Don’ts to prevent fire. These include messages regarding not carrying any inflammable material, explosives, prohibition of smoking inside the coaches, penalties etc.
- Production Units are providing Fire detection and suppression system in newly manufactured Power Cars and Pantry Cars, Fire and Smoke detection system in newly manufactured coaches. Progressive fitment of the same in existing coaches is also underway by Zonal Railways in a phased manner.
- Regular counselling and training of staff is undertaken.
- Concept of Rolling Block introduced in Indian Railways (Open Lines) General Rules vide Gazette notification dated 30.11.2023, wherein work of integrated maintenance/ repair/replacement of assets is planned up to 52 weeks in advance on rolling basis and executed as per plan.
The details of the Safety related works related to better maintenance practices, Technological improvements, better infrastructure and rolling stock etc. undertaken by Railways are tabulated below:-
|
S.N.
|
Item
|
2004-05 to 2013-14
|
2014-15 to 2024-25
|
2014-25 Vs. 2004-14
|
|
|
Technological Improvements
|
|
1.
|
Use of high-quality rails
(60 Kg) (Km)
|
57,450 Km
|
1.43 Lakh Km
|
More than 2 times
|
|
2.
|
Longer Rail Panels
(260m) (Km)
|
9,917 Km
|
77,522 Km
|
Nearly 8 times
|
|
3.
|
Electronic Interlocking (Stations)
|
837 Stations
|
3,691 Stations
|
More than 4 times
|
|
4.
|
Fog Pass Safety Devices (Nos.)
|
As on 31.03.14:
90 Nos.
|
As on 31.03.25: 25,939 Nos.
|
288 times
|
|
5.
|
Thick Web Switches (Nos.)
|
Nil
|
28,301 Nos.
|
|
|
|
Better Maintenance Practices
|
|
1.
|
Primary Rail Renewal (Track Km)
|
32,260 Km
|
49,941 Km
|
1.5 times
|
|
2.
|
USFD (Ultra Sonic Flaw detection) Testing of Welds (Nos.)
|
79.43 Lakh
|
2 Crore
|
More than 2 times
|
|
3.
|
Weld failures (Nos.)
|
In 2013-14: 3699 Nos.
|
In 2024-25:
370 Nos.
|
90 % reduction
|
|
4.
|
Rail fractures (Nos.)
|
In 2013-14: 2548 Nos.
|
In 2024-25:
289 Nos.
|
More than 88% reduction
|
|
|
Better Infrastructure and Rolling Stock
|
|
1.
|
New Track KM added (Track Km)
|
14,985 Km
|
34,428 Km
|
More than 2 times
|
|
2.
|
Flyovers (RoBs)/ Underpasses (RUBs) (Nos.)
|
4,148 Nos.
|
13,808 Nos.
|
More than 3 times
|
|
3.
|
Unmanned Level crossings
(Nos.) on BG
|
As on 31.03.14:
8,948
|
As on 31.03.24: Nil
(All eliminated by 31.01.19)
|
Removed
|
|
4.
|
Manufacture of LHB Coaches (Nos.)
|
2,337 Nos.
|
42,677
|
More than 18 times
|
This information was provided by the Union Minister for Railways, Information & Broadcasting and Electronics & Information Technology, Shri Ashwini Vaishnaw, in a reply to a question in Rajya Sabha today.
*****
Dharmendra Tewari/ Dr. Nayan Solanki/ Manik Sharma
(Release ID: 2202873)
Visitor Counter : 1485