PIB Headquarters
Crafted in India, Delivered Globally: Exports Powered by Trade Agreements
Posted On:
18 DEC 2025 7:17PM by PIB Delhi
|
Key Takeaways
- Between November 2024 and November 2025, India’s total exports rose from US$ 64.05 billion to US$ 73.99 billion, registering a strong 15.52% growth.
- India has inked a series of major Free Trade Agreements (FTAs), the most recent being the Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) with Oman. Active negotiations ongoing with several other countries.
- Export diversification is further poised to strengthen trade stability, competitiveness, and long-term economic security amid global uncertainties.
|
India’s Trade Story at a Glance
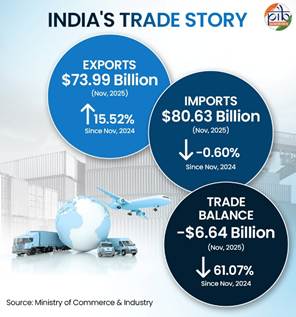
Driven by diversification, innovation, and strategic trade reforms, India continues to strengthen its position in global markets. From strong post-pandemic recovery to enduring global uncertainties, India’s exports are not just growing, they are setting new benchmarks. The year-on-year rise from November 2024 to November 2025 highlights India as a trusted and reliable partner in global trade.
Between November 2024 and November 2025, India’s total exports rose from US$ 64.05 billion to US$ 73.99 billion, registering a strong 15.52% growth, while imports remained largely stable at US$ 80.63 billion. Consequently, the trade deficit narrowed significantly by 61.07%, from US$ 17.06 billion to US$ 6.64 billion.Despite trade disruption, this growth reflects India’s resilience, with high-value commodities, widening global partnerships, and policy reforms supporting a more balanced and globally integrated trade trajectory.
For export growth India is also focused on enhancing its international trade relations. India's trade agreements with other economies reinforces its commitment to inclusive growth, benefiting farmers, artisans, workers, MSMEs while safeguarding core national interests. Most recently, the India–Oman agreement builds on long standing bilateral ties, creating a forward looking and balanced economic framework.
Powering Global Trade: India’s Export Journey
India’s exports recorded year-on-year growth in November 2025, reflecting sustained momentum in external trade. The increase was supported by higher export values across key merchandise and services sectors, alongside steady demand from major partner countries. This performance underscores the resilience of India’s export sector amid evolving global trade conditions.
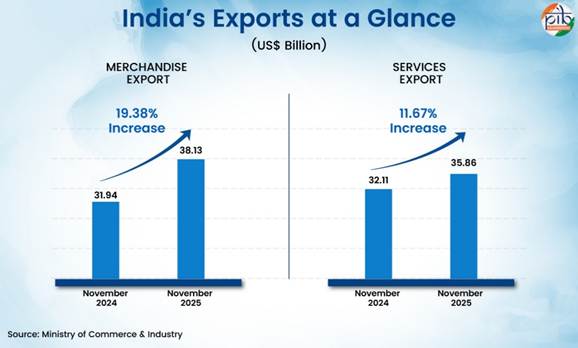
- Merchandise exports during November 2025 were US$ 38.13 Billion as compared to US$ 31.94 Billion in November 2024, registering a growth of 19.38% over the year.
- Services export for November 2025 is US$ 35.86 Billion as compared to US$ 32.11 Billion in November 2024, indicating growth of 11.67% in a year.
- The share of merchandise exports was 51.53%, whereas service exports constituted 48.47% share in total exports in November 2025.
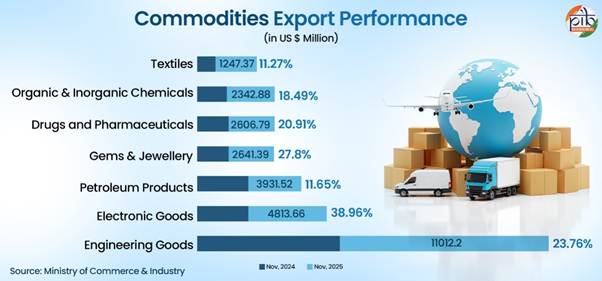
Readymade garments of all textiles, a labor-intensive sector, continue to contribute positively. Exports rose to USD 1247.37 Million with 11.27% increase in November 2025 compared to last year.Some of the large export markets for India which clocked impressive growth rates were UAE (14.5%), UK (1.5%), Japan (19.0%), Germany (2.9%), Spain (9.0%) and France (9.2%). On the other hand, some of the other markets that recorded higher growth rates were Egypt (27%), Saudi Arabia (12.5%), Hong Kong (69%) etc. This performance highlights the sector’s adaptability and competitiveness in the face of global uncertainties.
Similarly, Organic and Inorganic Chemicals exports grew by 18.49% over the year in November 2025. India’s drugs and pharmaceutical sector which is recognised as the Pharmacy of the World, experienced 20.19% growth in exports over the year. Indian pharma exports are destined to more than 200 countries around the globe including highly regulated markets of US, West Europe, Japan and Australia indicating diversification in this sector too.
Export of Gems and Jewellery also registered a growth of 27.8% in November, 2025. Indian jewellery is admired for its craftsmanship, design, and cultural richness. Demand is growing in key markets such as the United States, United Arab Emirates, Hong Kong, and Europe, especially for gold, diamond, and coloured gemstone jewellery.
India has witnessed a remarkable surge in petroleum product exports over the last decade. India is the seventh-largest exporter of refined petroleum products and ranks among the top five refining nations globally, due to its robust infrastructure and strategic geographic location. The export growth in November 2025 was 11.65% when compared from the corresponding year in the last year. Key export destinations include South Asian, African, and European countries.
Engineering goods, a traditional pillar of India’s exports, have recorded steady growth, with the US as the top destination, followed by the UAE, Germany, the UK, and Saudi Arabia. To sustain momentum, the government has rolled out measures such as Zero Duty EPCG and the Market Access Initiative (MAI) to support exporters and boost overseas revenues.
With a target of building a $500 billion domestic electronics ecosystem by 2030-31, India is now firmly on track to become a global leader in electronic design, manufacturing, and exports. Leading the way are mobile phones from just ₹1,500 crore in 2014-15, mobile phone exports reached ₹2 lakh crore in 2024-25, growing 127 times in a single decade. Indian electronics goods are now exported to major markets, with the top five destinations in FY 2024-25 being the United States, United Arab Emirates, Netherlands, the United Kingdom, and Italy.
Export Diversification: A Strategic Approach
Export diversification has emerged as a deliberate policy strategy. It helps navigate uncertain global trade environments marked by geopolitical tensions, demand volatility, and supply chain disruptions. By expanding across products and markets, countries reduce overdependence on limited partners and build resilience against external shocks. This approach strengthens trade stability, competitiveness, and long-term economic security amid global uncertainties.
Avoiding export instability and reducing dependency
Commodity dependent exports are inherently exposed to sharp price fluctuations, which can lead to instability in export earnings if countries rely on a narrow set of products. Such volatility may heighten macroeconomic uncertainty and dampen long-term investment decisions. Export diversification offers a pathway to greater stability by spreading risk across products and markets, thereby supporting sustained export growth and long-term economic resilience.
Building resilience against global demand shocks
Building resilience against global demand shocks is crucial, as limited export diversification can leave economies vulnerable to sudden downturns in global demand. Diversifying exports enhances the ability to absorb such economic shocks by spreading risk across sectors and markets, thereby ensuring greater stability in export performance.
Encouraging knowledge spillover
Export diversification fosters flow of ideas, skills, and information by encouraging the adoption of new production techniques, management practices, and marketing capabilities that can diffuse across industries. By expanding the range of export products, economies strengthen learning, innovation, and productivity, supporting higher per capita income growth over the long term.
Strengthening macroeconomic stability
Exports alone accounted for 21.2% of India’s GDP in 2024. Limited diversification can expose the economy to global uncertainties and export shortfalls, affecting macroeconomic stability. Export diversification strengthens stability by broadening economic activity, reducing vulnerability to external shocks, and supporting sustainable growth and improved living standards.
Expanding Global Ties: Unlocking Trade Opportunities for India
As India’s economic footprint continues to expand worldwide, it has emerged as a preferred partner for deeper trade and economic collaboration.
India and Oman sign CEPA: India’s 2nd FTA in the last 6 months after UK
DID YOU KNOW?
Oman is a key pillar of India’s West Asia Policy and India’s oldest strategic partner in the region. The strong economic partnership is reflected in 6,000+ India–Oman joint ventures operating in Oman.
|
India signed a Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) with Oman on 18 December 2025, marking a significant step in strengthening economic engagement with the Gulf region, as the two countries commemorate 70 years of diplomatic relations. The agreement underscores India’s growing stature as a trusted and dependable global trade partner.
- The agreement opens new export opportunities for India’s labour-intensive sectors- such as agriculture, textiles, leather, gems and jewellery, engineering, pharmaceuticals, and automobiles- supporting job creation and empowering artisans, women-led enterprises, and MSMEs.
- India held a 10.24% share in Oman’s agricultural imports in 2024, ranking second among suppliers. Major export items include Basmati rice, parboiled rice, bananas, potatoes, onions, meal of soyabean, sweet biscuits, cashew kernels, mixed condiments, butter, fish body oil, prawn & shrimps feed, frozen boneless bovine meat, and fertilized eggs.
- Duty free access to boneless meat of bovine animals, other fresh eggs, sweet biscuits, cashew kernels, other fats & oils derived from milk, other mixed condiments & seasonings, prepared/preserved potatoes, other egg yolks not dried, guar gum, kabuli chana and other cheese provide a competitive edge over other countries exporting to Oman.
- Elimination of the tariff from butter, sugar confectionery, bakery products, poultry meat & offal, mixed condiments & mixed seasoning, other fruit squash prepared/preserved, natural honey strengthens India’s position in Oman’s market.
- CEPA offers unprecedented market access for Indian goods with zero-duty access on 98.08% of Oman’s tariff lines, covering 99.38% of India’s exports by value.
- It marks the first-ever commitment by any country on traditional medicine across all modes opening significant opportunities for India’s wellness sectors and AYUSH, which anchors India’s traditional medicine sector through a comprehensive institutional framework.
- For the first time, Oman has offered commitments across key mode 4 categories, high quality temporary entry and temporary stay commitments for intra-corporate transferees, and contractual service suppliers, business visitors and independent professionals and liberalised entry and stay for professionals in accountancy, taxation, architecture, medical and allied sectors.
Besides, India has signed a series of major Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) with global economies, strengthening its position in international trade and opening new markets for Indian businesses.
- India concluded a Comprehensive Economic and Trade Agreement (CETA) with the United Kingdom in 2025. CETA provides an unprecedented duty-free access to 99% of India’s exports to the UK, covering nearly 100% of the trade value, benefiting sectors such as textiles, leather, marine products, gems, engineering goods, chemicals, and auto components.
- Notably, the agreement goes beyond goods and addresses services, a core strength of India’s economy. India exported over US$ 19.8 billion in services to the UK in 2023, and CETA promises to expand this further.
- Additionally, in a first by UK, mobility for professionals across IT, healthcare, finance, and education is being eased with CETA. This offers streamlined entry for contractual service suppliers, business visitors, intra-corporate transferees, independent professionals.
- Another major breakthrough is the Double Contribution Convention- that will save Indian firms and workers ₹4,000+ crore by removing the need for dual social security contributions.
- Marking its first FTA with four developed European nations, India signed a trade and economic partnership agreement with the EFTA countries- Switzerland, Norway, Iceland, and Liechtenstein- in 2024. The agreement improves market access for Indian pharmaceuticals, engineering goods, and services, backed by strong investment commitments, including USD 100 billion in investment and the creation of one million jobs in India.
- India’s Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) with the United Arab Emirates, signed in 2022, has substantially reduced tariffs on over 90%of Indian exports- particularly in gems and jewellery, textiles, leather, and engineering goods- supporting the target of exceeding $100 billion in bilateral trade.
- With Australia, India concluded the Economic Cooperation and Trade Agreement (ECTA) in 2022, eliminating or reducing tariffs on most traded goods. The agreement has opened the Australian market to Indian textiles, pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and agriculture.
- In Africa, India signed its first trade pact with the continent through the Comprehensive Economic Cooperation and Partnership Agreement (CECPA) with Mauritius in 2021. The agreement enables easier market access for Indian exporters while strengthening Mauritius’ role as a gateway to African markets.
Besides these concluded agreements, several major economies are currently engaged in active negotiations with India to deepen trade and investment ties through FTAs and comprehensive economic partnerships.

- India and Israel signed the Terms of Reference for an FTA in November 2025. The proposed pact is expected to deepen cooperation in sectors such as fintech, agri-tech, artificial intelligence, quantum computing, machine learning, pharmaceuticals, space and defence.
- India and the United States continue discussions on a bilateral trade agreement, with rounds of talks held in 2025. Under the ambitious "Mission 500", both countries aim to more than double US-India trade to $500 billion by 2030 to be achieved by deepening the trade relationship across multiple sectors.
- India is also in discussion with European Union (EU) for an FTA. Technical discussions on key chapters of the FTA such as market access for goods, rules of origin, services, technical barriers to trade, trade and sustainable development etc. took place in December 2025.
- Discussions for the ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA) is also underway, which holds potential to unleash the full economic potential of the member countries and further strengthen regional cooperation.
- The India-Australia Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement (CECA) negotiations are advancing, covering a wide range of areas including goods, services and mobility, digital trade, rules of origin, legal and institutional provisions, environment, labour, and gender, bringing greater understanding for convergence in the remaining provisions.
- India and Mexico meetings have been centered on strengthening bilateral trade and investment relations, with discussions focused on expanding trade, investment, expanding economic cooperation, fostering business collaborations, and exploring opportunities across diverse sectors.
- Negotiations are also underway with New Zealand for an FTA or Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement with key tracks including trade in goods, trade in services, economic and trade cooperation, and rules of origin. The proposed FTA is expected to significantly enhance trade flows, deepen investment linkages, strengthen supply-chain resilience, and provide greater predictability and market access for businesses.
- With Canada, India continues discussions on a Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement, supported by agreed terms of reference. The proposed agreement aims to raise bilateral trade to around $50 billion by 2030 through tariff reductions and clearer frameworks for services and investment.
- India is actively negotiating an FTA with the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) and exploring a similar arrangement with Qatar, with the objective of strengthening ties across trade, energy, investment, and security.
The expanding network of concluded agreements and ongoing negotiations reflects a broader shift in India’s international economic engagement. Together, these partnerships position India to play a central role in shaping contemporary trade architectures anchored in mutual growth, resilience, and strategic trust.
Boosting India’s Export Competitiveness
The Government has implemented a comprehensive set of policy and institutional measures to strengthen India’s export ecosystem. These measures are strengthening India’s export competitiveness and integration with global markets.
Export Promotion Mission
The Export Promotion Mission, was approved on 12 November, 2025, with a total outlay of Rs.25,060 crore for FY 2025–26 to FY 2030–31. The mission operates through two integrated sub-schemes, Niryat Protsahan and Niryat Disha. Niryat Protsahan focuses on improving access to affordable trade finance for MSMEs through a range of instruments. Niryat Disha focuses on non-financial enablers that enhance market readiness and competitiveness, such as export quality and compliance support, assistance for international branding, packaging and others.
The integration of 29 labour laws into four Labour Codes has streamlined compliance, enhanced industrial efficiency, and strengthened worker protection. The reforms provide export-oriented industries with simplified regulations, flexible hiring provisions, unified registrations and returns, and expanded social security coverage, while ensuring occupational safety and welfare. At the same time, workers benefit from universal minimum wages, timely and transparent wage payments, mandatory appointment letters, grievance redressal mechanisms, and comprehensive social security protection.
Since 22 September 2025, Next Gen GST 2.0 reforms have come into effect. 90% provisional refunds for zero rated supplies and inverted duty structure claims are being provided on a system driven, risk-based basis. The removal of value-based threshold limits for GST refunds on exports supports small exporters by enabling refund claims on low-value consignments. GST rate reductions across packaging materials, textiles, leather, wood, trucks, delivery vans, toys, and sports goods lower production, freight, and logistics costs, enhance export competitiveness, and support domestic manufacturing. Further, revised place of supply rules for “intermediary services” enables Indian service exporters to claim export related benefits, while correction of inverted duty structures in textiles and food processing eases working capital pressures and reduces refund dependency.
India’s other export promotion schemes comprise targeted government initiatives to reduce costs, strengthen infrastructure, improve quality standards, and enhance export competitiveness. The Foreign Trade Policy 2023 provides incentive-based support, promotes market diversification, and enables closure of legacy authorisations, while the RoDTEP (Remission of Duties and Taxes on Exported Products) scheme reimburses embedded duties and taxes, with ₹58,000 crore disbursed up to March 2025.
Export ecosystems are being strengthened through the initiatives such as Districts as Export Hubs which are making states and districts active players in trade. 734 districts have been identified with export potential while District Export Action Plans (DEAP) has been prepared for 590 districts. The role of Special Economic Zones is also significant in the trade promotion, as it recorded exports of ₹14.56 lakh crore in FY 2024–25.
Infrastructure and manufacturing competitiveness are being enhanced through the Trade Infrastructure for Export Scheme (TIES), PM GatiShakti, the National Logistics Policy. The Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme, launched in 2020 is boosting manufacturing across 14 sectors, has attracted ₹1.76 lakh crore investments, generated ₹16.5 lakh crore in output, and created over 12 lakh jobs by March 2025. Further support is being provided through ease of doing business reforms and digital trade platforms such as the National Single Window System, Trade Connect e-Platform, E-Commerce Export Hubs, and ICEGATE.
Conclusion
India’s export performance between over the recent years reflects steady momentum, marked by diversification across products and markets and a balanced contribution from merchandise and services exports. The export basket recorded higher export values across major commodities. The export growth was accompanied by deeper engagement with key partner countries and emerging markets, supported by continued policy and procedural reforms. Together, these trends underscore India’s evolving export profile and its deepening integration with global trade networks.
Reference
Prime Minister's Office
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2193304®=3&lang=1
Ministry of Commerce and Industry
https://indiantradeportal.in/vs.jsp?lang=0&id=0,959,10581,28177,28189#:~:text=The%20India%2DUAE%20CEPA%20is,%2C%20and%20Japan%20(PMDA)
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2189383®=3&lang=2
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2186809®=3&lang=2
https://www.commerce.gov.in/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/LS-USQ-No.4971-dated.-01.04.2025.pdf
https://gjepc.org/pdf/Gem-&-Jewellery-Half-Yearly-Report-H1-FY2025-Final.pdf
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2201284®=3&lang=2
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2187705®=3&lang=2
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2192819®=3&lang=2
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2204071®=3&lang=2
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2205889®=3&lang=1
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2201138®=3&lang=1
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2182724®=3&lang=2
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2160190®=3&lang=2
High Commission of India Port Louis
https://hcimauritius.gov.in/pages?id=9avme&subid=Pe9xd&nextid=axk9e
DD News
https://ddnews.gov.in/en/india-australia-mark-three-years-of-ecta-pledge-to-strengthen-economic-partnership/
https://ddnews.gov.in/en/indias-electronics-surge-powers-jobs-exports-and-global-industry-growth/#:~:text=India's%20electronics%20industry%20has%20undergone,(FDI)%20in%20electronics%20manufacturing
https://ddnews.gov.in/en/india-negotiating-fta-with-gcc-and-qatar-mea/
PIB Archives
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2177724®=3&lang=2
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressNoteDetails.aspx?NoteId=152038&ModuleId=3®=3&lang=2
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressNoteDetails.aspx?NoteId=154945&ModuleId=3®=3&lang=2
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2175702®=3&lang=2
https://www.pib.gov.in/FactsheetDetails.aspx?Id=150511®=3&lang=1
Ministry of Textiles
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2189312®=3&lang=2
Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers
https://pharma-dept.gov.in/pharma-industry-promotion
Ministry of Petroleum & Natural Gas
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2096817®=3&lang=2
World Bank
https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/server/api/core/bitstreams/e8eb01ea-1588-5e80-83cd-a0b9c51c685f/content
https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/NE.EXP.GNFS.ZS?locations=IN
IMF
https://www.imf.org/-/media/files/publications/wp/2018/wp1886.pdf
https://www.imf.org/-/media/files/publications/dp/2024/english/eddpea.pdf
ASEAN
https://asean.org/member-states/
Click here to see in PDF
PIB Research
(Release ID: 2206194)
Visitor Counter : 6368