Ministry of Textiles
YEAR END REVIEW 2025 OF MINISTRY OF TEXTILES
PM MITRA Scheme Witnesses Significant Progress in 2025 with Infrastructure Works Initiated, DPRs Approved and Foundation Stone Laid at Dhar
Textile and Apparel Exports Registers Growth in 2025, reaching USD 37.8 Billion and Reinforcing India’s Global Trade Presence
PLI Scheme for Textiles Records tangible Outcomes with Investments Reported, Production Commenced and Incentives Disbursed
Cotton Sector Reforms to Support Farmers through MSP Procurement, Digitization and Productivity Initiatives
Bharat Tex 2025 Showcased India’s Textile Strength, Innovation and Global Leadership at Scale
Posted On:
24 DEC 2025 1:10PM by PIB Delhi

1. PM MITRA:
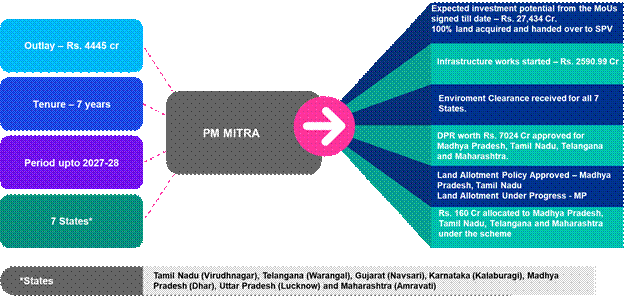
The Government has approved setting up of 7 (Seven) PM Mega Integrated Textile Region and Apparel (PM MITRA) Parks in Greenfield/Brownfield sites with world class infrastructure including plug and play facility with an outlay of Rs. 4445 cr for a period of seven years upto 2027-28. The Government has finalized 7 sites viz. Tamil Nadu (Virudhnagar), Telangana (Warangal), Gujarat (Navsari), Karnataka (Kalaburagi), Madhya Pradesh (Dhar), Uttar Pradesh (Lucknow) and Maharashtra (Amravati) for setting up PM MITRA Parks.
-
- So far investment MoUs with expected investment potential of over Rs. 27,434/- crore have been signed. 100% land acquired and handed over to SPV.
-
- Post approval of sites by the Government, Infrastructure works worth Rs 2590.99 Cr for providing infrastructure till the park gates have been started by all seven State Governments.
-
- Environment Clearance received for all PM MITRA Parks. The foundation stone of the PM MITRA Park Dhar, Madhya Pradesh was laid by the Hon’ble Prime Minister on 17thSeptember, 2025.
-
- DPR worth Rs. 7024 Cr. has been approved for PM MITRA Park Madhya Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Telangana and Maharashtra.
-
- Land allotment policy for PM MITRA Park Madhya Pradesh and Tamil Nadu approved and land allotment in Dhar, Madhya Pradesh is under progress.
-
- Total Rs. 160 Cr. has been assigned to PM MITRA Park Madhya Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Maharashtra and Telangana.
2. NATIONAL TECHNICAL TEXTILES MISSION (NTTM)
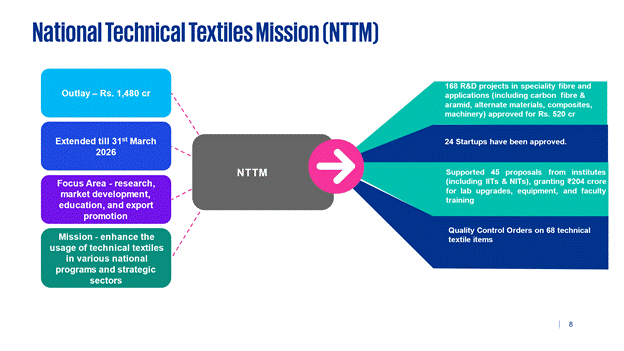
The Government has launched the National Technical Textiles Mission (NTTM) with an outlay of Rs. 1,480 crores, focusing on research, market development, education, and export promotion. The mission aims to enhance the usage of technical textiles in various national programs and strategic sectors and has been extended until 31stMarch 2026.
2.1 168 R&D projects in speciality fibre and applications (including carbon fibre & aramid, alternate materials, composites, machinery) approved for Rs. 520 cr.
2.2 24 Startups have been approved.
2.3 To support education, training & skilling, 45 proposals from educational institutes, including IITs & NITs supported for introducing new degree programs/ papers for UG/PG under technical textiles, with total grant of Rs. 204 cr. for upgrading lab, equipment, and training of faculty.
2.4 8 Quality Control Orders on 68 technical textile items.
- PRODUCTION LINKED INCENTIVE (PLI) TEXTILES
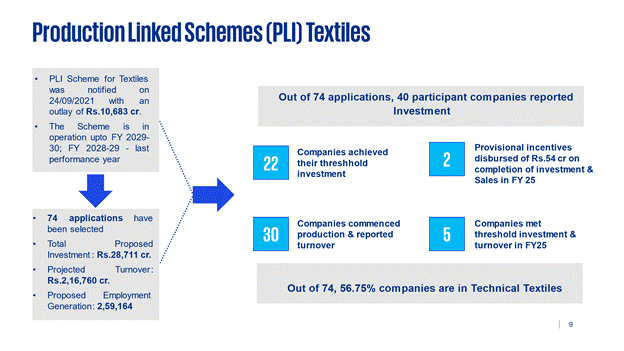
PLI Scheme for Textiles was notified on 24/09/2021 with an objective to promote production of MMF Apparel & Fabrics and products of Technical Textiles in the country to enable textile industry to achieve size and scale, become competitive, create employment opportunities for people and support creation of a viable enterprise and competitive textile industry with an approved outlay of Rs.10,683 cr. The Scheme had two years of gestation period from FY: 2022-23 and FY: 2023-24. The Scheme is in operation upto FY 2029-30; FY 2028-29 being last performance year.
3.1 74 applications were selected under the scheme. The total proposed investment would be Rs.28,711 cr., projected turnover of Rs.2,16,760 cr. and proposed employment generation of 2,59,164.
3.2 40 Participant companies reported investment.
- 22 Companies have achieved their threshold investment.
- 30 Participant companies commenced production and reported turnover.
- Disbursed provisional incentive of Rs.54 cr. to two applicants who completed their threshold Investment and Sales in FY 2024-25.
- 5 companies reported to have met threshold investment & turnover in 2024-25.
3.3 From 74 companies 56.75% are in field of Technical Textile (TT). TT is more capital intensive as compared to other two segment of MMF Apparel & MMF fabrics.
4. TEXTILES TRADE PROMOTION (TTP)
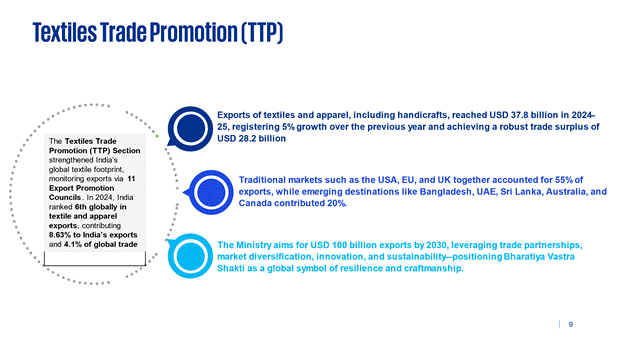
The Textiles Trade Promotion (TTP) Section has played a pivotal role in strengthening India’s global textile footprint, monitoring export performance through eleven Export Promotion Councils. In 2024India emerged as the 6th largest exporter of textiles and apparel, with the sector contributing a significant 8.63% share to India’s total exports and accounting for 4.1% of global trade.
4.1 Exports of textiles and apparel, including handicrafts, reached USD 37.8 billion in 2024–25, registering 5% growth over the previous year and achieving a robust trade surplus of USD 28.2 billion.
4.2 Traditional markets such as the USA, EU, and UK together accounted for 55% of exports, while emerging destinations like Bangladesh, UAE, Sri Lanka, Australia, and Canada contributed 20%.
4.3 With over 500 districts across 33 States/UTs actively engaged, the Ministry has set a bold Vision 2030 target of USD 100 billion exports, to be driven by enhanced trade partnerships, market diversification, and a strong focus on innovation and sustainability—underscoring India’s BharatiyaVastra Shakti as a symbol of resilience, craftsmanship, and global competitiveness.
5. SAMARTH SCHEME
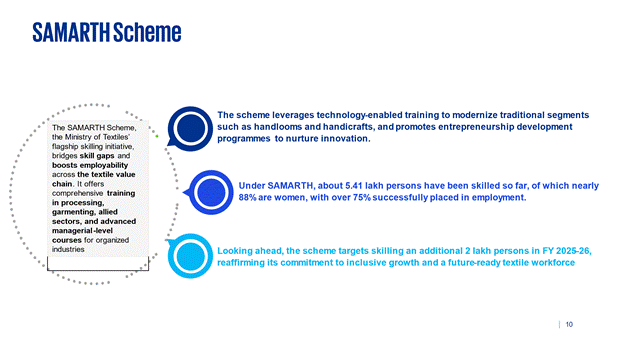
The SAMARTH Scheme, the Ministry of Textiles’ flagship skilling initiative, has emerged as a transformative force in bridging skill gaps and enhancing employability across India’s textile value chain. It provides a comprehensive training ecosystem covering processing, garmenting, and allied sectors, while also offering advanced, long-term, and managerial-level courses for organized industries.
5.1 The scheme leverages technology-enabled training to modernize traditional segments such as handlooms and handicrafts, and promotes entrepreneurship development programmes to nurture innovation.
5.2 Under SAMARTH, about 5.41 lakh persons have been skilled so far, of which nearly 4.76 lakh (88%) are women, with over 4.05 lakh (75%) successfully placed in employment.
5.3 Looking ahead, the scheme targets skilling an additional 2 lakh persons in FY 2025–26, reaffirming its commitment to inclusive growth and a future-ready textile workforce.
6. COTTON SECTOR:
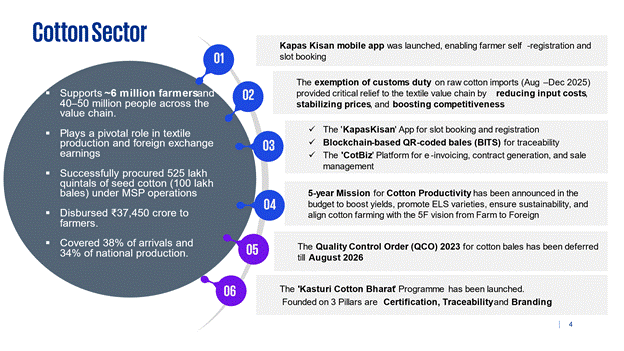
The cotton sector, a cornerstone of India’s agricultural economy supporting nearly 6 million farmers and 40–50 million people across the value chain, continues to play a pivotal role in textile production and foreign exchange earnings. In the cotton season 2024–25, the Government through its nodal agency, the Cotton Corporation of India Ltd. (CCI) under Ministry of Textiles has successfully procured 525 lakh quintals of seed cotton (100 lakh bales) under MSP operations, disbursing ₹37,450 crore to farmers—covering 38% of arrivals and 34% of national production.
-
- To enhance transparency, the Kapas Kisan mobile app was launched, enabling farmer self-registration and slot booking.
- The exemption of customs duty on raw cotton imports (Aug–Dec 2025) provided critical relief to the textile value chain by reducing input costs, stabilizing prices, and boosting competitiveness.
- Reforms by digitization of procurement of cotton under MSP operations- The 'KapasKisan' App for slot booking and registration. Blockchain-based QR-coded bales (BITS) for traceability. The 'CotBiz' Platform for e-invoicing, contract generation, and sale management.
- A 5-year Mission for Cotton Productivity has been announced in the budget to boost yields, promote ELS varieties, ensure sustainability, and align cotton farming with the 5F vision from Farm to Foreign.
- The Quality Control Order (QCO) 2023 for cotton bales has been deferred till August 2026.
- The 'Kasturi Cotton Bharat' Programme has been launched, founded on the three pillars of Certification, Traceability, and Branding, to enhance the global market acceptance of Indian cotton. Collectively, these measures strengthen farmer welfare, stabilize markets, and reinforce India’s textile and apparel sector as a driver of employment and export growth.
7. WOOL SECTOR:
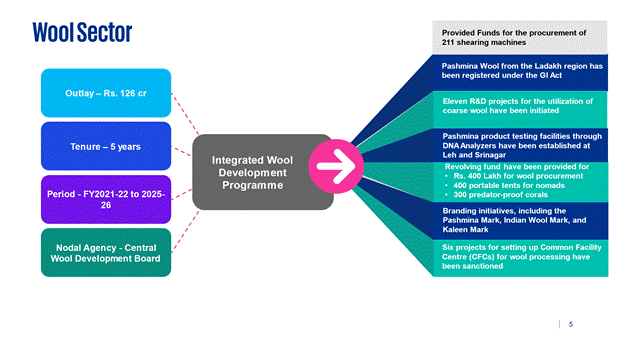
For the holistic growth of the Wool Sector, the Ministry of Textiles has formulated Integrated Wool Development Programme, (IWDP) for implementation during the period of 15thFinance Commission i.e., from FY 2021-22 to 2025-26 with total financial allocation of Rs. 126 Crore through approval of its SFC meeting held on 15th June 2021. IWDP scheme of MOT is Central Sector Scheme for Development of Wool Sector. Further, the Guidelines of IWDP has been approved by MoT and appointed Central Wool Development Board, Ministry of Textiles as nodal agency for implementation of this scheme in all major wool producing States.
7.1 Pashmina Wool from the Ladakh region has been registered under the GI Act.
7.2 Eleven R&D projects for the utilization of coarse wool have been initiated.
7.3 Pashmina product testing facilities through DNA Analysers have been established at Leh and Srinagar.
7.4 Funds for the procurement of 211 shearing machines have been provided across several states.
7.5 A revolving fund of Rs.400 Lakh for wool procurement, 400 portable tents for nomads, and 300 predator-proof corals have been provided.
7.6 Branding initiatives, including the Pashmina Mark, Indian Wool Mark, and Kaleen Mark have been initiated.
7.7 Six projects for setting up Common Facility Centre (CFCs) for wool processing have been sanctioned across various locations.
8. SILK SECTOR:
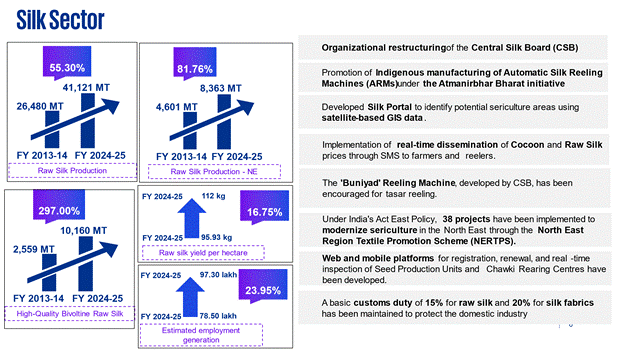
The annual raw silk production has increased to 41,121 MT during 2024-25 from 26,480 MT in 2013-14, indicating a growth of 55.30%. In the North-Eastern (NE) States, raw silk production rose from 4,601 MT to 8,363 MT, showing an increase of 81.76%. The production of high-quality bivoltine raw silk increased significantly from 2,559 MT in 2013-14 to 10,160 MT in 2024-25, marking a growth of 297%. India continues to hold the second position globally in total silk production. Raw silk yield per hectare has increased to 112 kg during 2024-25 as compared to 95.93 kg during 2013-14, with an improvement of 16.75%. Estimated employment generation increased to 97.30 lakh persons during 2024-25 from 78.50 lakh persons during 2013-14, reflecting a growth of 23.95%.
8.1 Organizational restructuring of the Central Silk Board (CSB) has been undertaken for enhanced efficiency.
8.2 Indigenous manufacturing of Automatic Silk Reeling Machines (ARMs) has been promoted under the Atmanirbhar Bharat initiative.
8.3 The SILKS Portal has been developed to identify potential sericulture areas using satellite-based GIS data.
8.4 Real-time dissemination of cocoon and Raw Silk prices through SMS to farmers and reelershas been implemented.
8.5 The 'Buniyad' Reeling Machine, developed by CSB, has been encouraged for tasar reeling, eliminating thigh reeling and protecting women's dignity.
8.6 Under India's Act East Policy, 38 projects have been implemented to modernize sericulture in the North East through the North East Region Textile Promotion Scheme (NERTPS).
8.7 Web and mobile platforms for registration, renewal, and real-time inspection of Seed Production Units and Chawki Rearing Centres have been developed.
4.8 A basic customs duty of 15% for raw silk and 20% for silk fabrics has been maintained to protect the domestic industry.
9. JUTE SECTOR:
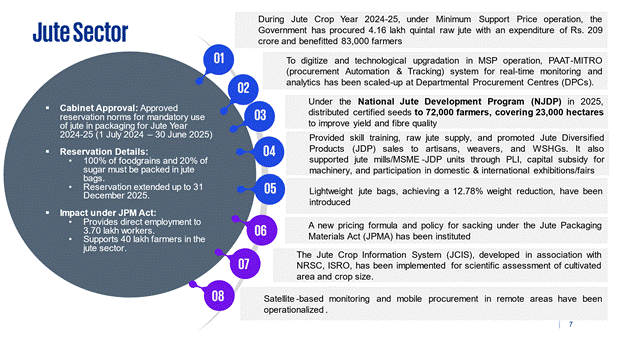
The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs has approved reservation norms for mandatory use of jute in packaging for the Jute Year 2024-25 (1stJuly, 2024 to 30th June, 2025) for 100% reservation of the foodgrains and 20% of sugar to be compulsorily packed in jute bags. This reservation has been extended upto 31.12.2025. The reservations norms under JPM Act provide for direct employment to 3.70 lakh workers and 40 lakh farmers in the Jute Sector.
-
- During Jute Crop Year 2024-25, under Minimum Support Price operation, the Government has procured 4.16 lakh quintal raw jute with an expenditure of Rs. 209 crore and benefitted 83,000 farmers.
- To digitize and technological upgradation in MSP operation, PAAT-MITRO (procurement Automation & Tracking) system for real-time monitoring and analytics has been scaled-up at Departmental Procurement Centres (DPCs).
- The Government has been implementing an Umbrella Program, National Jute Development Program (NJDP) for development and promotion of Jute Sector. During year 2025, the Government under Jute-Improved Cultivation and Advanced Retting Exercise scheme of NJDP has distributed certified seeds to 72,000 jute farmers through covering 23,000-hectare land for enhancing yield and fibre quality.
- The Government has provided skill Training, supply of raw jute, promotion of Jute Diversified Product(JDP) sale, to Artisans, weavers, WSHGs, etc. Also, supported jute mills/ MSME-JDP units through Production Linked Incentive, Capital Subsidy for Plant &Machinery, participation in Exhibitions, fairs in the country and foreign, under the program.
- Lightweight jute bags, achieving a 12.78% weight reduction, have been introduced.
- A new pricing formula and policy for sacking under the Jute Packaging Materials Act (JPMA) has been instituted.
- The Jute Crop Information System (JCIS), developed in association with NRSC, ISROhas been implemented for scientific assessment of cultivated area and crop size.
- Satellite-based monitoring and mobile procurement in remote areas have been operationalized.
10. NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF FASHION TECHNOLOGY (NIFT)
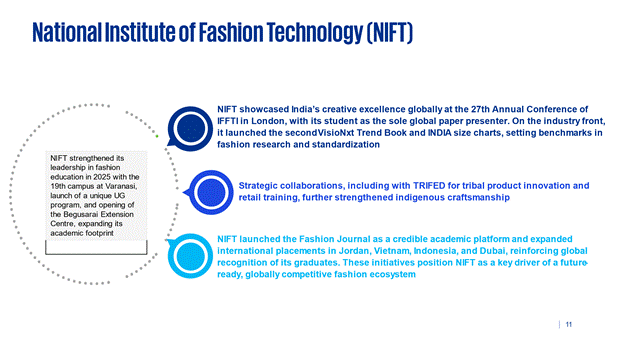
The National Institute of Fashion Technology (NIFT) has reinforced its leadership in fashion education and innovation during 2025 with landmark achievements. The establishment of the 19th campus at Varanasi, launch of a unique UG programme, and inauguration of the Begusarai Extension Centre expanded its academic footprint.
10.1 Internationally, NIFT showcased India’s creative excellence at the 27thAnnual Conference of the International Foundation of Fashion Technology Institutes in London, where its student was the sole global paper presenter. On the industry front, the second VisioNxt Trend Book and India-specific size charts under INDIAsize were released, setting new benchmarks for fashion research and standardization.
10.2 Strategic collaborations, including with TRIFED for tribal product innovation and retail training, further strengthened indigenous craftsmanship.
10.3 The launch of the NIFT Fashion Journal provided a credible academic platform, while expanding international placements in Jordan, Vietnam, Indonesia, and Dubai underscored the growing global recognition of NIFT graduates. Collectively, these initiatives highlight NIFT’s pivotal role in shaping a future-ready, globally competitive fashion ecosystem.
11. HANDLOOM SECTOR
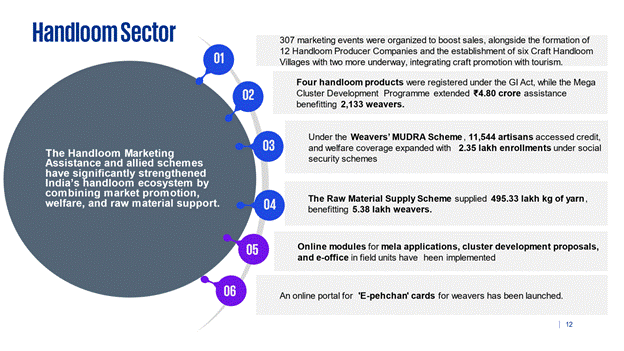
The Handloom Marketing Assistance and allied schemes have significantly strengthened India’s handloom ecosystem by combining market promotion, welfare, and raw material support.
11.1 307 marketing events were organized to boost sales, alongside the formation of 12 Handloom Producer Companies and the establishment of six Craft Handloom Villages with two more underway, integrating craft promotion with tourism.
11.2 Further, four handloom products were registered under the GI Act, while the Mega Cluster Development Programme extended ₹4.80 crore assistance benefitting 2,133 weavers.
11.3 Under the Weavers’ MUDRA Scheme, 11,544 artisans accessed credit, and welfare coverage expanded with 2.35 lakh enrollments under social security schemes.
11.4 Complementing these efforts, the Raw Material Supply Scheme supplied 495.33 lakh kg of yarn, benefitting 5.38 lakh weavers, thereby ensuring productivity, sustainable livelihoods, and enhanced incomes across the sector.
11.5 Online modules for mela applications, cluster development proposals, and e-office in field units have been implemented for transparency and efficiency.
11.6 An online portal for 'E-pehchan' cards for weavers has been launched.
12. HANDICRAFT SECTOR
The Office of the Development Commissioner (Handicrafts) under the aegis of Ministry of Textiles implements two schemes namely National Handicrafts Development Programme (NHDP) and Comprehensive Handicrafts Cluster Development Scheme (CHCDS) for overall development and promotion of handicrafts sector across the country.
12.1 1.30 lakh artisans have been registered and issued artisans ID card under “Pehchan”.
12.2 67 Handicraft Producer Companies have been approved and necessary handholding supports are being provided to these PCs. 922 different interventions have been sanctioned in various handicraft clusters across the country with total project cost of ₹59.13 Crores benefitting 32398 artisans.
12.3 462 Marketing events 1225 CDAP have been organised with total project cost of ₹101.05 Crores benefitting 26873 artisans. 746 Design development programmes have been conducted with total project cost of ₹32.82 Crores benefitting 28840 artisans.
12.4 517 skill training programmes have been conducted with total project cost of ₹41.57 Crores benefitting 15510 artisans. 162 Research & Development programmes have been conducted with total project cost of ₹21.84 Crores benefitting 5495 artisans.
12.5 The lndiaHandmade.com e-commerce portal has been launched. The BharatiyaVastraEvamShilpaKosh portal was inaugurated.
12.6 A special focus on women-led entrepreneurs ('Shilpi Didi') has been instituted.
13. QCO Reform
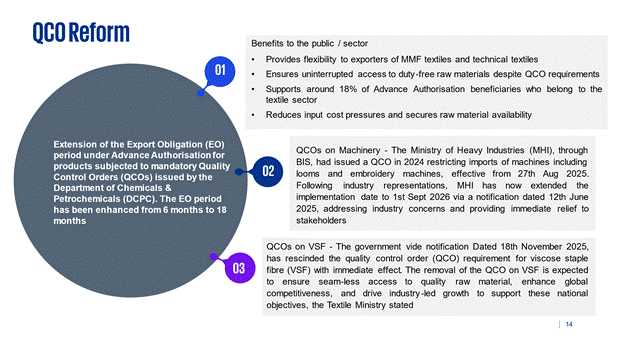
Extension of the Export Obligation (EO) period under Advance Authorisation for products subjected to mandatory Quality Control Orders (QCOs) issued by the Department of Chemicals & Petrochemicals (DCPC). The EO period has been enhanced from 6 months to 18 months.
13.1 Benefits to the public / sector
- Provides flexibility to exporters of MMF textiles and technical textiles.
- Ensures uninterrupted access to duty-free raw materials despite QCO requirements.
- Supports around 18% of Advance Authorisation beneficiaries who belong to the textile sector.
- Reduces input cost pressures and secures raw material availability.
13.2 QCOs on Machinery - The Ministry of Heavy Industries (MHI), through BIS, had issued a QCO in 2024 restricting imports of machines including looms and embroidery machines, effective from 27th Aug 2025. Following industry representations, MHI has now extended the implementation date to 1st Sept 2026 via a notification dated 12th June 2025, addressing industry concerns and providing immediate relief to stakeholders.
13.3 QCOs on VSF - The government vide notification Dated 18thNovember 2025, has rescinded the quality control order (QCO) requirement for viscose staple fibre (VSF) with immediate effect. The removal of the QCO on VSF is expected to ensure seam-less access to quality raw material, enhance global competitiveness, and drive industry-led growth to support these national objectives, the Textile Ministry stated.
14. Export Oriented Reforms:

In order to address the impact of US Tariff Impact, following reforms undertaken:
14.1 The Remission of Duties and Taxes on Exported Products (RoDTEP) scheme has been extended to unit in EOUs/SEZs and units with Advance Authorisation until 31.03.2026.
14.2 The Rebate of State and Central Taxes and Levies (RoSCTL) scheme for garment and made-up exports have been extended until 31.03.2026, with the process for a further extension initiated. End-to end digitisation has been implemented.
14.3 The period for export obligation under Advance Authorisation has been extended from 6 to 18 months for cases seeking QCO exemption.
14.4 Data-driven, mapping of 520 exporting districts has been completed.
14.5 A Minimum Import Price (MIP) on Synthetic Knitted Fabric items has been imposed until 31.03.2026, and an effective import monitoring system has been developed.
15. GST Reforms:

Next-Generation GST Rationalisation in Textiles (as per recommendations of the 56th GST Council Meeting).
15.1 Readymade Garments & Made ups): 5% GST rate up to ₹2,500/piece (earlier ₹1,000) on items of readymade garments and made ups (excluding HS other than 63053200, 63053300, 6309).
15.2 Man-Made Fibres& Yarns: GST reduced from 18%→5% (fibres) and 12%→5% (yarns). This corrects the inverted duty structure (IDS), aligns fibre–yarn–fabric rates, and removes long-standing working capital burdens on manufacturers.
15.3 Carpets & Floor Coverings (HS 5701–5705): GST reduced from 12% to 5%. This will boost exports from clusters such as Bhadohi and Srinagar, strengthen traditional crafts, and improve affordability in domestic markets.
15.4 Handicrafts & Handlooms: GST reduced from 12% to 5% on 36 handicraft items, cotton rugs of handloom, and handwoven carpets under HS 5705. This measure will provide relief to artisans, enhance rural livelihoods, and support India’s rich craft traditions.
15.5 Sewing Machines (domestic and industrial covered under HS 8452): GST reduced from 12% to 5%, easing costs for tailoring units and boosting domestic manufacturing.
16. Regulatory and Legal Reforms:

As part of the Jan Vishwas (Amendment of Provisions) Bill, 2025, the Ministry of Textiles has rationalised punitive provisions across key legislations to promote ease of doing business and reduce compliance burden.
16.1 The Central SiIk Board Act, 1948 - Sections 14A, 14(1) (a), 14(1) (b), and 14(1)(c) prescribing imprisonment or fines have been proposed for decriminalisation.
16.2 The Textile Committee Act, 1963 - Sections 17(2)(a), 17(2)(b), and 18(1) involving penal provisions have been recommended to convert criminal liabilities into civil penalties.
16.3 The Handloom (Reservation of Articles for Production) Act, 1985 - Sections 10(a), 11(a), and 11(b) have been proposed for decriminalisation, aligning with broader government initiatives to enhance regulatory trust-based governance.
17. BHARAT Tex 2025:

India's largest global textile event, was successfully organized from February 14 to 17, 2025, at Bharat Mandapam, New Delhi.
17.1 The event spanned 2.2 million square feet and featured over 5,000 exhibitors, providing a comprehensive showcase of India's textile ecosystem. More than 1,20,000 trade visitors, from 120+ countries including global CEOs, policymakers, and industry leaders, attended the event. The event showcases 12000+ Textiles products, 6000+ Overseas Buer, 120,000 Trade visitors and 70+ knowledge session.
17.2 Bharat Tex 2025 served as a platform to accelerate the government's "Farm to Fibre, Fabric, Fashion, and Foreign Markets" vision. India’s textile exports have already reached ₹3 lakh crore, and the goal is to triple this to ₹9 lakh crore by 2030 by strengthening domestic manufacturing and expanding global reach.
17.3 The event demonstrated India's leadership in the textile sector and its commitment to innovation, sustainability and global collaboration.
*********
MAM/VN
(Release ID: 2208051)
Visitor Counter : 5297