PIB Headquarters
CERT-In: India’s Frontline Defender against Cyber Threats
Building a Safe, Trusted and Accountable Cyberspace
Posted On:
23 JAN 2026 9:45AM by PIB Delhi
Key Takeaways
- In 2025, CERT-In handled over 29.44 lakh cyber incidents, issuing 1,530 alerts, 390 vulnerability notes, and 65 advisories, reflecting large-scale national cyber response capability.
- 231 cybersecurity audit organisations empanelled, significantly strengthening audit and vulnerability assessment capacity across critical Information Communication Technology infrastructure.
- 98% digital population covered by Cyber Swachhta Kendra, 1,427 organisations onboarded, and 89.55 lakh malware removal tool downloads.
- CERT-In’s sustained cybersecurity efforts have earned global recognition, with leading international platforms such as the World Economic Forum, the University of Oxford, and France’s ANSSI acknowledging India’s leadership in AI-driven threat detection, cyber resilience, trusted AI frameworks, and citizen-centric malware mitigation.
Introduction
India’s rapid digital transformation has reshaped governance, commerce, and citizen services at an unprecedented scale. From digital payments and e-commerce to online public service delivery, digital technology has become integral to everyday life. As digital adoption accelerates, safeguarding cyberspace has emerged as a national priority.
With rising instances of online fraud, phishing, ransomware attacks, AI-driven scams, and threats to critical digital infrastructure, the need for a coordinated and resilient cybersecurity framework has never been greater. Recognising this challenge, the Government of India has put in place robust policies, institutional mechanisms, and operational capabilities to ensure a safe, trusted, and secure digital environment.
At the centre of India’s cybersecurity architecture is the Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In), operating under the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) and mandated by the Information Technology Act, 2000. CERT-In provides the institutional depth for national cyber defence by overseeing incident management, enhancing systemic resilience, and promoting secure digital practices across government, industry, and society. Its work underpins the protection of India’s rapidly expanding digital ecosystem and supports confidence in digital platforms and services.
In today’s interconnected digital landscape, cybersecurity is no longer a purely technical concern but a foundational pillar of national security, economic stability, and public trust. The scale and complexity of digital systems demand continuous vigilance, coordinated action, and strong institutional leadership. By combining policy direction with operational readiness, CERT-In not only responds to emerging cyber threats but also anticipates risks, builds resilience, and ensures that India’s digital growth remains secure, inclusive, and sustainable.
India’s Expanding Digital Landscape
Over the last decade, India’s digital footprint has grown exponentially. It is driven by rising internet penetration, widespread smartphone adoption, and the rapid expansion of digital public services. By 2025, internet connections in India crossed the milestone of 100 crore, reaching 100.29 crore, compared to 25.15 crore in March 2014. Average monthly data consumption per wireless data subscriber increased nearly 399 times, rising from 61.66 MB in 2014 to 24.01 GB in 2025, among the highest globally.
This strong digital foundation has enabled remarkable growth in digital payments. The Unified Payments Interface (UPI) has emerged as the central pillar of India’s digital payment ecosystem. In December 2025 alone, UPI processed over 21 billion transactions valued at more than ₹27 lakh crore. While this digital expansion has significantly enhanced convenience and inclusion, it has also widened the attack surface for cyber threats. To address these risks, the Union Budget 2025–26 allocated ₹782 crore for cybersecurity, underscoring the government’s strong focus on securing India’s digital infrastructure.
In this context, CERT-In’s role assumes critical importance as the cornerstone of India’s cybersecurity framework. CSIRT-Fin i.e. Computer Security Incident Response Team for the Financial Sector functioning under CERT In, strengthens cybersecurity in the financial sector by enabling coordinated incident response, information sharing, and providing guidance and support for the Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance (BFSI) sector. Similarly CSIRT-Power works as an extended arm of CERT-In for fortifying the cybersecurity posture of the Power Sector by coordinating and analysing cyber incidents, acting on cyber threat intelligence from CERT-In, taking proactive containment measures based on situational awareness details provided by CERT-In, ensuring cybersecurity audits are carried out and mitigating vulnerabilities as reported by CERT-In’s Cyber Swachhta Kendra (CSKs).
Core Functions of CERT-In for the National Cybersecurity
CERT-In is the national agency for cyber incident response in India. Its mandate under section 70B of the Information Technology (IT) Act 2000 includes the prevention of cyberattacks, real-time monitoring of cyber threats, and swift coordination with stakeholders to mitigate and contain cyber incidents.
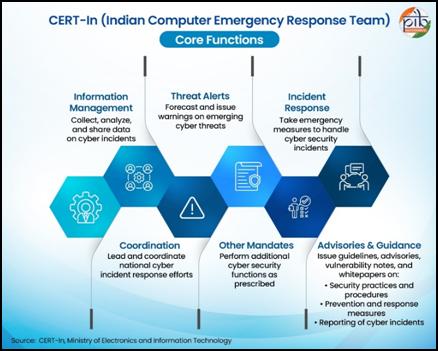
Core functions of CERT-In includes:
- Promoting cybersecurity awareness among organisations and citizens,
- Facilitating information sharing through its automated cyber threat exchange platform,
- Sharing near-real time information on existing and potential cyber threats with organisaitons covering all sectors,
- Collaborating with international partners, industry and academia,
- Conducting regular training programmes, cybersecurity exercises/drills
- Operating CSKs for ensuring cyber hygiene & a Command & Control Center for facilitating monitoring of cyber threats and attack campaigns
- Coordinating mitigation measures with organisations and stakeholders during significant national and international activities,
- Institutionalising responsible vulnerability disclosure
- Supporting incident investigations & supporting law enforcement agencies through its cyber forensics capabilities,
- Enabling organisations & providing guidance on cyber crisis management plan implementation to enhance national preparedness.
Through sustained operational engagement and coordinated response mechanisms, CERT-In ensures rapid containment of cyber incidents and supports the restoration of affected systems across sectors. Its continuous flow of actionable intelligence and guidance enables stakeholders to strengthen preparedness, reduce systemic risk, and respond effectively to evolving threats. Together, these efforts contribute to minimising disruption, accelerating recovery, and reinforcing confidence in India’s digital ecosystem.
CERT-In at the Core of India’s Cyber Resilience Strategy
CERT-In continues to serve as the cornerstone of India’s national cyber defence architecture through proactive threat detection, rapid incident response, and large-scale capacity building. Its achievements in 2025 reflect a sustained and systematic effort to strengthen institutional resilience, secure critical digital infrastructure, and reinforce trust in India’s rapidly expanding digital ecosystem.
|
An overview of CERT-In’s Key achievements of 2025
- National Cyber Incident Response and Threat Intelligence
- In 2025, CERT-In handled over 29.44 lakh cyber incidents, issuing 1,530 alerts, 390 vulnerability notes, and 65 advisories, reflecting large-scale national cyber response capability.
- 29 Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVEs) were identified and published by CERT-In.
- Cybersecurity Audits
- CERT-In empaneled 231 certified security audit organisations to strengthen cybersecurity across government, public, and private sector ICT systems .
- A majority of these audits were carried out in the banking and financial institutions, power and energy, and transport sectors.
- Capacity Building
- CERT-In conducted 32 specialised technical training programmes and 95 cybersecurity awareness sessions for government, PSU, and private-sector stakeholders.
- Trained 20,799 officers and cybersecurity professionals across government, PSUs, and industry through specialised capacity-building programmes.
- Cybersecurity Drills and Preparedness Exercises
- CERT-In conducted 122 cybersecurity drills and exercises of varying complexity, including tabletop exercises, with participation from about 1,570 organisations across government, public, and private sectors (Defence, Paramilitary Forces, Space, Atomic Energy, Telecommunications (ISPs), Finance, Power, Oil and Natural Gas, Transportation, IT/ITeS sectors, and State Data Centres).
- Awareness Initiatives
- CERT-In conducted 95 awareness sessions covering 91,065 participants (including National Cybersecurity Awareness Month (NCSAM) October 2025).
|
In 2025, CERT-In also published a comprehensive suite of reports, whitepapers, guidelines, advisories, and vulnerability notes, providing timely, actionable guidance to organisations and stakeholders for proactive cyber risk mitigation and resilience building.
Reports & Guidelines Published in 2025
- Cybersecurity Guidelines for Smart City Infrastructure (February 2025)
- Advisory on Cybersecurity threats and best practices for satellite communications (Feb 2025)
- India Ransomware Report (March 2025)
- Digital Threat Report 2024 for the BFSI (Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance) sector (April 2025)
- White paper on “Good Practices for protecting Unmanned Aircraft Systems (UAS) against Cybersecurity Threats” (April 2025)
- Technical Guidelines on SBOM (Software Bill of Materials), QBOM &CBOM (Quantum Bill of Materials and Cryptographic Bill of Materials), HBOM (Hardware Bill of Material), AIBOM (Artificial Intelligence Bill of Materials) Version 2 (July 2025)
- Comprehensive Cybersecurity Audit Policy Guidelines (July 2025)
- White paper on Transitioning to Quantum Cyber Readiness (July 2025)
- 15 Elemental Cyber Defense Controls for Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs)- (Sep 2025)
- During NCSAM October 2025, published a “Cyber Smart Kids: Suraksha Guide”.
- Cybersecurity Best Practices for Senior Citizens - booklet.
CERT-In’s achievements in 2025 reflect its central role in safeguarding India’s rapidly expanding digital ecosystem. Through large-scale capacity building, rigorous audits, continuous awareness efforts, and the release of forward-looking guidelines and technical frameworks, CERT-In has strengthened institutional preparedness across government, industry, and society.
Institutional Frameworks anchored by CERT-In
To operationalise national cybersecurity policy and translate strategic intent into on-ground action, CERT-In anchors a set of specialised institutional frameworks. These mechanisms provide structured coordination, preventive safeguards, and rapid response capabilities across sectors, States, and citizens.
- The Cyber Swachhta Kendra (CSK) the CSK (Botnet Cleaning and Malware Analysis Centre) is established by CERT-In to enhance cyber hygiene among citizens. The centre tracks networks of internet connected devices such as computers, mobile phones, IoT devices, and home routers—that are infected with malware. It provides free tools and guidance to help users clean infected devices and works closely with industry, academia, and internet service providers to identify compromised systems and alert users. Regular awareness campaigns promote safe online behaviour and responsible digital practices.
|
As of December 2025, CSK covers 98% of India’s digital population, sending large-scale notifications on botnet and malware infections. Engaging 1,427 organisations across key sectors, it helps detect and remediate malware, while 89.55 lakh downloads of its free botnet-removal tools underscore CSK’s role as a citizen-centric, preventive cybersecurity initiatives.
|
- Security Assurance Framework CERT-In operates a security assurance framework to strengthen the security of government and critical sector systems. Under this framework; certified IT security audit organisations conduct regular audits; Vulnerability assessments and penetration testing are undertaken; and Audit findings are analysed to identify common weaknesses. Based on these insights, CERT-In issues secure design guidelines and promotes best practices. Regular audits under this framework significantly enhance cyber readiness and resilience across sectors.
- National Cyber Coordination Centre (NCCC) NCCC, implemented by CERT-In, monitors cyberspace at metadata level to detect potential cybersecurity threats for situational awareness. It facilitates real-time information sharing with concerned organisations, State governments, and other stakeholders, enabling timely preventive and response actions.
- Computer Security Incident Response Teams (CSIRTs) CERT-In oversees a network of CSIRTs operating at the sectoral and State/UT levels. Sectoral CSIRTs support domains such as finance, power, and telecom, while State CSIRTs operate under respective State and UT governments.
- Cyber Crisis Management Plan (CCMP) CERT-In has also developed a CCMP for government bodies, providing structured guidance during major cyberattacks and cyber-terrorism incidents. The plan supports rapid response, recovery, and continuity of essential services, particularly for critical infrastructure.
Collectively, these institutional frameworks enable a whole-of-government and whole-of-society approach to cybersecurity. By integrating prevention, preparedness, response, and recovery. It ensures that India’s digital ecosystem remains resilient, adaptive, and secure amid evolving cyber threats. This layered institutional design strengthens national readiness while safeguarding critical infrastructure and citizens alike.
Global Recognition of India’s Cybersecurity Leadership
CERT-In’s sustained domestic efforts have increasingly resonated at the global level. Its operational scale, technology-driven approaches, and emphasis on collaborative cyber governance have positioned India as a credible and responsible stakeholder in the international cybersecurity ecosystem.
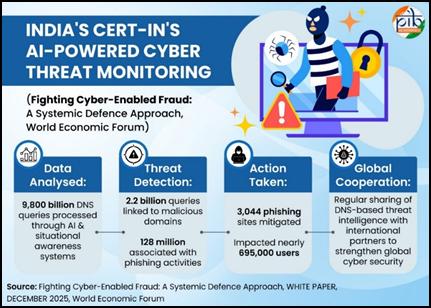
- In the Global Cybersecurity Outlook 2025 published by the World Economic Forum (WEF), CERT-In has been highlighted for its deployment of AI-driven situational awareness systems to analyse and detect malicious domains and phishing activities, as well as for its real-time sharing of threat intelligence at the global level.
- In April 2025, CERT-In contributed to the Cyber Resilience Compass paper published jointly by the WEF and the University of Oxford, which identified seven critical domains of cyber resilience.
- In February 2025, CERT-In was among the international partners to co-sign the joint high-level risk analysis report on Artificial Intelligence titled “Building Trust in AI through a Cyber-Risk-Based Approach”, published by France’s National Cybersecurity Agency (ANSSI). The report advocates a risk-based approach to enable trusted AI systems, secure AI value chains, and address emerging AI-related cyber risks.
Together, these recognitions underscore CERT-In’s growing influence and leadership in shaping global cybersecurity and AI risk governance. They underscore CERT-In’s emerging role in shaping global discussions on cyber resilience, threat intelligence sharing, and responsible AI risk governance.
Conclusion
Amid the growing complexity and scale of cyber threats, CERT-In continues to anchor India’s cybersecurity ecosystem. Through continuously identifying and mitigating cyber risks, CERT-In has significantly strengthened national cyber resilience. Its initiatives, ranging from institutional frameworks and sectoral & state CSIRTs to citizen-centric awareness programmes, demonstrate a comprehensive and forward-looking approach to securing India’s ICT infrastructure and protecting users. International recognition of CERT-In’s AI-driven innovations further underscores India’s growing leadership in cybersecurity. Collectively, these sustained efforts reaffirm the Government of India’s commitment to safeguarding cyberspace and ensuring a safe, trusted, and secure digital future for all citizens.
References
Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology
Ministry of Communications
Ministry of Home Affairs
PIB Headquarters:
the420.in
click here to see pdf
****
PIB Research
(Release ID: 2217537)
Visitor Counter : 4536