Industries
Threads of Reform
प्रविष्टि तिथि:
17 SEP 2025 15:41 PM
GST Reforms in Textiles, Apparel, and Logistics
September 17, 2025
Key Takeaways
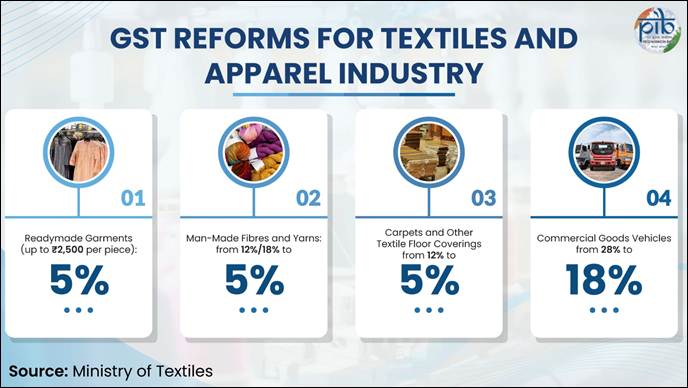
- GST on readymade garments up to ₹2,500 per piece is now 5%, making apparel more affordable and boosting domestic demand.
- GST on man-made fibres and yarns cut from 12%/18% to 5% removes inverted duty structure and strengthens Small and Medium Enterprises.
- GST on carpets and other textile floor coverings reduced from 12% to 5%, enhancing global competitiveness
- GST on commercial goods vehicles lowered from 28% to 18%, cutting logistics costs and supporting exports
Introduction
The recent rationalisation of Goods and Services Tax (GST) rates marks a significant reform aimed at removing structural anomalies, reducing costs, and boosting demand across critical sectors. These changes are particularly impactful in the textile and logistics industries, both of which are vital for domestic growth, employment, and export competitiveness.
By aligning tax rates across the value chain, the GST reform ensures affordability for consumers, sustains jobs in labour-intensive sectors, and enhances India’s ability to compete globally. In the textile sector, the rationalisation strengthens the entire value chain—from fibre to garment—by reducing distortions, improving garment affordability, reviving retail demand, and supporting export competitiveness.
These reforms are expected to deliver far-reaching benefits, correcting long-standing anomalies while building a stronger foundation for the “Make in India” initiative and positioning the country as a global manufacturing hub.
Indian Government Initiatives to Promote Indian Textile Industry
The Government of India has been working tirelessly to promote Indian textiles. To boost production, the government has approved the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme for Textiles in September 2021 (with an outlay of ₹10,683 crore), targeting MMF fabrics, MMF apparel, and Technical Textiles, to boost large-scale manufacturing and global competitiveness. The government is actively promoting exports through schemes like Rebate of State and Central Taxes and Levies (RoSCTL) and Remissions of Duties and Taxes on Exported Products (RoDTEP) to rebate/reimburse state, central taxes and duties on exports (especially for apparel, garments, made-ups). The government supports infrastructure via PM-MITRA Textile Parks, and promotes innovation and skill enhancement through the National Technical Textiles Mission and the SAMARTH scheme.
Readymade Garments & Apparel
GST at 5% up to ₹2,500 per piece (earlier limit was ₹1,000)

Impact of the increased limit:
- Affordable apparel for middle- and low-income households – expanding the lower slab reduces costs for mass-market buyers.
- Stimulating domestic demand – higher consumption expected, with significant impact in small towns and rural regions.
- Labour-intensive growth – greater demand leads to more employment opportunities in garment manufacturing, especially for women.
- Support for ‘Make in India’ – lower tax helps domestic brands and exporters compete effectively against cheap imports in the low- and mid-price segments.
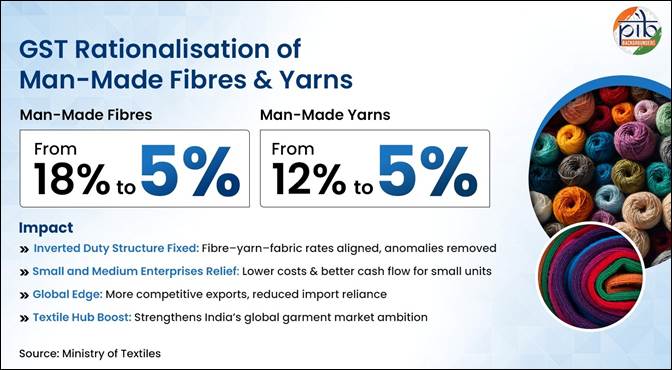
Man-Made Fibres & Yarns
Man-Made Fibres GST reduced from 18% to 5%; Man-Made Yarns cut from 12% to 5%
Impact of the reduced GST rates:
- Resolution of Inverted Duty Structure (IDS) – aligns fibre, yarn, and fabric rates, removing longstanding anomalies that increased working capital burden for manufacturers.
- Strengthening Small and Medium Enterprises – many MMF producers are small and medium units; lower GST improves cash flows and reduces cost burdens.
- Global competitiveness – Indian synthetic textiles become more price-competitive, reducing reliance on imports and boosting exports.
- Support to textile hub ambition – positions India as a major player in the international MMF-based garment market, supporting India’s ambition to become a global textile hub.
Carpets & Other Textile Floor Coverings
GST reduced from 12% to 5%
This cut enhances affordability in domestic markets and makes Indian carpets more competitive internationally, boosting a traditional sector with strong export potential.

Logistics
GST on Commercial Goods Vehicles (trucks, delivery-vans, etc) down from 28% to 18%
The GST reforms also extend to the transport sector, which plays a crucial role in reducing logistics costs and supporting industrial growth. Trucks and delivery vans, which carry nearly 65–70% of India’s goods traffic, benefit significantly from tax rationalisation.
Key Benefits to the Textile Industry from Cheaper Logistics:
- Cheaper freight movement – reduced cost per tonne-km benefits the transport of textile, FMCG, and e-commerce deliveries.
- Inflation control – cascading effect of lower logistics cost helps reduce overall price pressures.
- Export competitiveness – lower logistics costs make Indian textiles more competitive abroad.
Conclusion
The GST rationalisation across textiles and logistics sectors is a decisive step towards strengthening India’s manufacturing base, improving affordability, and boosting exports. By reducing structural anomalies and easing cost pressures, these reforms directly benefit consumers, small businesses, and exporters alike. They reinforce the vision of a globally competitive India powered by resilient supply chains and a thriving textile sector.
References
Ministry of Textiles
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2152545
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2146758
Click here for pdf file
****
SK | M
(तथ्य सामग्री आईडी: 150293)
आगंतुक पटल : 468
Provide suggestions / comments
इस विश्लेषक को इन भाषाओं में पढ़ें :
हिन्दी