Social Welfare
Breaking Barriers: Gender Budgeting as a Catalyst for Inclusion
Posted On:
03 JUL 2025 12:40PM
Introduction
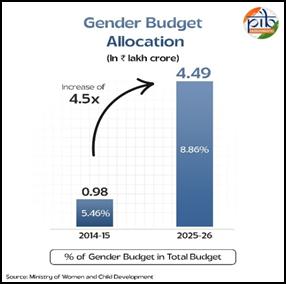
From 2014-15 to 2025-26, there has been a significant jump in the allocation for Gender Budgeting in India. The outlay has increased from ₹0.98 lakh crore in 2014-15 to ₹4.49 lakh crore in 2025-26, with the percentage share for Gender Budgeting in the Union Budget surging to a robust 8.86% in FY 2025-26, up from 5.46% in 2014-15[1]. This reflects the government’s sustained commitment to advancing gender equity through public spending.
India marked a major milestone in its efforts to make government budgets and spending more equitable and supportive of women with the introduction of the Gender Budget Statement in 2005–06. This marked the country's commitment to examining public resource allocation through a gender lens. It recognizes that national budgets don't impact all sections of society equally, necessitating a systematic approach to ensure women's developmental needs receive adequate attention in government spending.
 Gender budgeting is gaining momentum as more ministries and departments become aware of gender issues and start reviewing their programs and schemes with a gender-sensitive approach. This analytical tool serves not merely as an accounting exercise but as a strategic mechanism to ensure women’s needs are included in all government work, checks if services are reaching women, and aims to improve women’s access to public resources in India’s development plans.[2]
Gender budgeting is gaining momentum as more ministries and departments become aware of gender issues and start reviewing their programs and schemes with a gender-sensitive approach. This analytical tool serves not merely as an accounting exercise but as a strategic mechanism to ensure women’s needs are included in all government work, checks if services are reaching women, and aims to improve women’s access to public resources in India’s development plans.[2]
Components of India’s Gender Budgeting Framework
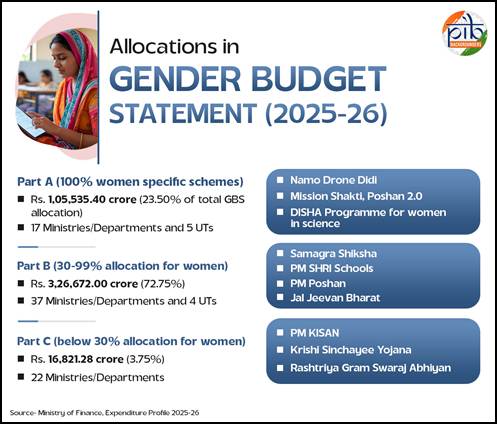
The Gender Budget is divided into two parts- the budget provisions for schemes that are substantially meant for the benefit of women. [3]
- Part A details schemes in which 100% provision is for women.
- Part B reflects schemes where the allocations for women constitute at least 30% of the provision.
- In the Union Budget of 2024-25, Part C was included as schemes with allocations for women and girls below 30% of the provision.[4] Inclusion of Part C in the GBS is expected to holistically reflect the allocations for women by the Government and its commitment towards gender equality and women empowerment.[5]
Evolution of Gender Budgeting in India
 [6]
[6]
Gender Budget: Union Budget 2025-26- Expenditure Statement
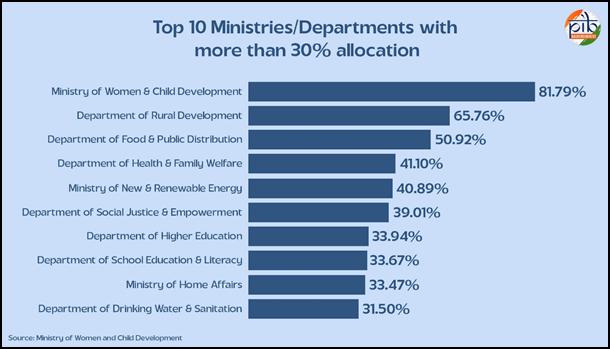
Top 10 Ministries/Departments that have reported more than 30% of their allocations in the Gender Budget for FY 2025-26:
Gender Budget: Positive Trends
As per a paper by the Observer Research Foundation, titled- ‘Gender-Responsive Budgeting in India, Bangladesh and Rwanda: A Comparison’ (July 2020), India’s introduction of gender budget shows a positive trend:
- India has institutionalized gender-responsive budgeting (GRB) at both national and state levels, with Gender Budget Cells established across ministries and departments.
- The mandatory inclusion of Gender Budget Statements (GBS) in the Union Budget ensures regular tracking of allocations for women and girls.
- Capacity-building initiatives, such as manuals, handbooks, and training by the Ministry of Women and Child Development, have strengthened technical expertise in gender budgeting.
- Several states have adopted GRB, promoting decentralized and region-specific gender interventions.
- There is an increasing emphasis on collecting sex-disaggregated data and monitoring outcomes, moving beyond input-based accounting to impact assessment.
- Gender budget allocations have steadily increased over the years, reflecting a growing financial commitment to gender equality.
- GRB has influenced the design of new women-centric schemes, enhancing women’s economic and social empowerment across sectors.
These trends collectively demonstrate India’s progress in mainstreaming gender considerations into public expenditure and policy planning.
Conclusion
Gender budgeting in India represents a transformative governance reform that transcends mere resource allocation to address deep-rooted structural inequalities and promote inclusive development. The remarkable growth in gender budget allocation from 6.8% to 8.86% in FY 2025-26, coupled with the evolution of a comprehensive three-part framework and the launch of Mission Shakti, demonstrates India's unwavering commitment to mainstreaming gender concerns across all government activities. The establishment of the Gender Budgeting Knowledge Hub portal and the active participation of ten major ministries allocating over 30% of their budgets to gender initiatives signal a paradigm shift toward evidence-based, gender-responsive policymaking. By embedding a gender lens into every aspect of planning, budgeting, and implementation, India is positioning itself as a global leader in gender-responsive governance, paving the way for a more equitable and inclusive society where every woman can realize her full potential.
References:
Ministry of Finance:
Ministry of Women and Child Development:
Observer Research Foundation:
Click here for pdf file
*****
SK/RK
(Backgrounder ID: 154811)
आगंतुक पटल : 6833
Provide suggestions / comments