Social Welfare
Sabka Saath Sabka Vikas Sabka Vishwas Sabka Prayas
Posted On:
09 JUN 2025 9:21AM
“Bharat is changing, and it is changing rapidly. People’s self-confidence, their trust in the government, and the commitment to build a new Bharat is visible everywhere.”
- PM Narendra Modi
Key Takeaways
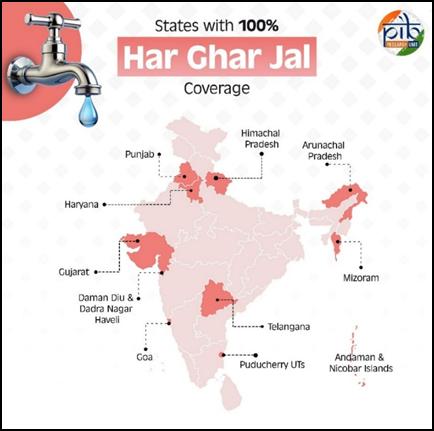
- 15.59 crore rural households now have tap water connections; 100% Har Ghar Jal in 8 states and 3 UTs.
- Nearly 4 crore houses completed; 92.35 lakh delivered under PMAY-U, with over 90 lakh owned by women.
- 2.86 crore households electrified under SAUBHAGYA; 22.6 hours average rural supply.
- Swachh Bharat Mission: 12 crore household toilets built; 5.64 lakh villages declared ODF Plus.
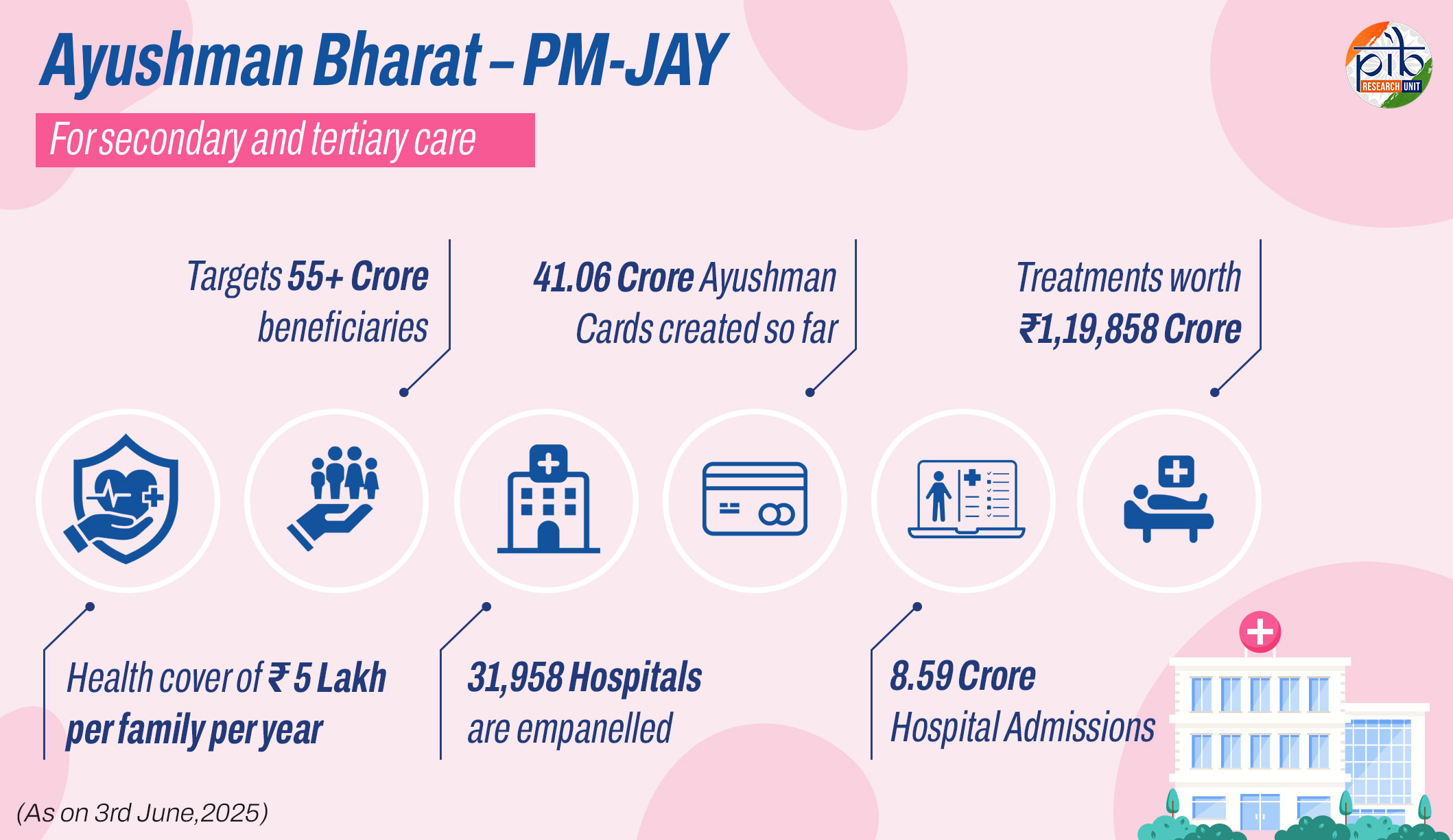
- Ayushman Bharat: Covers 55 crore people; benefits extended to all citizens 70+ under Ayushman Vay Vandana.
- Free ration to 81 crore beneficiaries; ₹11.80 lakh crore outlay till 2028.
- Over 10.33 crore LPG connections provided under PM Ujjwala Yojana.
- 68 lakh loans to street vendors under PM SVANidhi; 76.28 lakh vendors formalized.
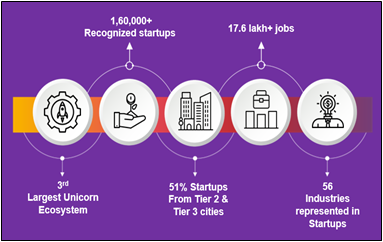
- 1.57 lakh startups recognized; 118 unicorns.
- 2.37 million artisans registered in PM Vishwakarma.
- eShram Portal: 30.86 crore unorganised workers registered; 53.75% women.
- Viksit Bharat Sankalp Yatra reached 2.6 lakh gram panchayats, 4,000 ULBs to ensure saturation of welfare schemes.
Introduction: Towards an Inclusive Bharat
Since 2014, India’s welfare architecture has been guided by the principle of Antyodaya—ensuring the upliftment and development of every person in the country. This philosophy has marked a decisive shift to inclusive empowerment, with the government targeting 100% saturation in every flagship scheme. Over the past eleven years, crores of previously deprived households have gained access to essential amenities such as tap water, electricity, toilets, housing, healthcare, clean cooking fuel, insurance, and digital services for the first time. These targeted, inclusive efforts have delivered measurable outcomes. A recent IMF working paper credited the Indian government with effectively ending extreme poverty in India. The 2023 Global Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI), released by United Nations Development Programme (UNDP), affirmed a significant decline across all ten indicators of multidimensional poverty in India. These achievements reflect a new era of governance—rooted in equity, backed by data, and powered by the resolve to serve every citizen.
India’s Triumph in Combating Poverty
India has achieved significant milestones in its fight against poverty, underscoring its commitment to uplifting the most vulnerable. According to the World Bank’s Spring 2025 Poverty and Equity Brief, the nation has lifted 171 million people out of extreme poverty over the past decade. The share of the population living on less than $2.15 per day fell sharply—from 16.2% in 2011–12 to just 2.3% in 2022–23.
At the $3.65 per day benchmark for lower-middle-income countries, poverty declined from 61.8% to 28.1%, translating to 378 million people moving above this line. Furthermore, India’s Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI)—which accounts for deprivations beyond income, including health, education, and living standards—dropped from 53.8% in 2005–06 to 16.4% in 2019–21. These achievements reflect a transformative shift in the lives of millions and mark a critical step forward in India’s mission to serve the poor and marginalized.
Empowering Progress: Higher Standards of Living and Formalisation of Jobs
Rising Standards of Living
In rural India, the average Monthly Per Capita Consumption Expenditure (MPCE) has risen from ₹1,430 in 2011–12 to ₹4,122 in 2023–24—a nearly threefold increase. Similarly, urban MPCE increased from ₹2,630 to ₹6,996 during the same period. This upward trend underscores improved purchasing power and access to a wider range of goods and services. Importantly, the share of food in total consumption has decreased (from 52.90% to 47.04% in rural areas), indicating a shift toward spending on education, healthcare, housing, and durable goods.
Increasing Formalisation of Jobs
The Employees' Provident Fund Organization (EPFO) has released provisional payroll data for March 2025, revealing a net addition of 14.58 lakh members. The year-on-year analysis reveals an increase of 1.15% in net payroll additions compared to March 2024, signifying increased employment opportunities and heightened awareness of employee benefits.
EPFO enrolled around 7.54 lakh new subscribers in March 2025, representing a 0.98% year-over-year growth compared to the previous year in March 2024.
Ensuring Provision of Basic Amenities to All
Clean Water, Healthier Lives: Jal Jeevan Mission
Building on this inclusive approach, one of the most fundamental services—access to clean drinking water—was addressed with renewed urgency. A mission that directly uplifted rural life, especially for women and children, was launched. The Jal Jeevan Mission (JJM) – Har Ghar Jal redefined access and dignity. More than 15.59 crore rural households now have tap water connections. Over 12 crore of these were added in just the past five years. Tribal and aspirational districts have seen substantial gains, with 7,275 Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups villages and 25,962 tribal villages now fully saturated. More than 9.35 lakh schools now have tap water access, securing the health of future generations.
A Home of One's Own: Housing for All
For many families across rural and urban India, a permanent house was once an unattainable dream. The Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (PMAY) changed that narrative. PMAY has two components: Urban and Grameen. A total of nearly 4 crore houses have been completed under PMAY.
Under PMAY - Urban, more than 92.72 lakh homes have been delivered, with over 90 lakh houses owned by women.
In rural India, 2.77 crore houses have been completed under PMAY - Grameen. Notably, 60% of these houses have been allocated to SCs and STs, and 25.29% have been registered in the name of women, promoting gender equity.
Lighting Up Lives: From Darkness to Electricity for All
Until recently, millions of rural homes lived in the hope of an electricity connection. With the launch of SAUBHAGYA and Deendayal Upadhyaya Gram Jyoti Yojana, that began to change. Today, 2.86 crore households have been electrified under the SAUBHAGYA scheme. The average rural electricity supply has surged from 12.5 hours in 2014 to 22.6 hours in 2025, significantly improving quality of life and economic productivity. Under the Deendayal Upadhyaya Gram Jyoti Yojana (DDUGJY) scheme, 100% village electrification has been achieved, lighting up aspirations in every corner of India.
From Illness to Assurance: Ayushman Bharat and Beyond
Ayushman Bharat
Ayushman Bharat was introduced to reduce the high out-of-pocket healthcare expenses, improve access to quality primary and secondary healthcare, and provide financial protection to poor and vulnerable families, thereby moving towards Universal Health Coverage. Ayushman Bharat - Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PM-JAY) offers free health insurance coverage to 55 crore Indians, making it the world’s largest health assurance scheme. The government, further, launched Ayushman Vay Vandana scheme for extending this coverage to all citizens aged 70 and above, regardless of income. The Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission complements this with over 77 crore Ayushman Bharat Health Accounts, linking citizens to seamless healthcare services.
Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojana
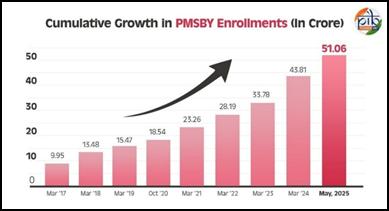
The Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojana (PMSBY) has played a vital role in extending affordable social security to millions, reinforcing the government’s commitment to a more inclusive and secure society. As of May 2025, the scheme has achieved a cumulative enrolment of 51.06 crore individuals, showcasing its extensive reach.
PM Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana (PM JJBY)
PM Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana (PM JJBY) is a one-year life insurance scheme, which can be renewed every year. It provides coverage of Rs 2 lakh in case of death due to any reason at a premium of Rs 436 per year. As of May 2025, 23.64 crore people are covered by PM JJBY.
Clean India, Healthy India: Sanitation and Swachh Bharat

India’s sanitation challenge was once a blot on its development journey. Swachh Bharat Mission was introduced to eliminate open defecation, improve solid waste management, and promote cleanliness and hygiene across India, aiming to improve public health and ensure dignity, especially for women and the poor. So far, the Swachh Bharat Mission has delivered over 12 crore household toilets across the country.
Over 5.64 lakh villages have now been declared Open Defecation Free (ODF) Plus, drastically reducing disease burden, especially among children and women.
Food Security for All
Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana (PMGKAY) was launched with the objective of mitigating hardships faced by the poor and needy due to economic disruptions caused by COVID -19 in the country. This scheme responded with scale and speed, providing free rations to 81 crore people since April 2020. With a planned outlay of Rs. 11.80 lakh crore till 2028, the scheme is the world’s largest social welfare programme, ensuring that no Indian sleeps hungry.
Cooking with Dignity: Clean Energy for Women

Traditional cooking methods using firewood posed serious health hazards to the lives of rural women. The Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana (PMUY) has provided 10.33 crore LPG connections, giving millions of women freedom from smoke and drudgery. As of March 2025, 32.94 crore people are active LPG consumers, making clean cooking the new norm.
Education and Employment: 10% EWS Reservation
The EWS reservation of 10% in employment and admission in educational institutions has been implemented as per the Constitution (one hundred and three) Amendment Act 2019. The annual family income limit of Rs. 8 lakh to identify EWS beneficiaries has been fixed by the government.
Street to Stability: Ensuring Financial Security of the Poor and Marginalised
A higher standard of living among the people called for financial inclusion, business opportunities, and social protection. Multiple schemes focused on enabling economic stability for the poor.
PM Mudra Yojana
The Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana provides access to institutional finance up to Rs 20 lakh to micro and small business units for income generating activities like manufacturing, trading, services, and agriculture related activities. Key highlights include:
- As of March 2025, more than 52.77 crore loan accounts have been extended since the inception of the scheme.
- Sanctioned amount: of Rs. 34.11 lakh crore
- Disbursed amount of Rs. 33.33 lakh crore.
- More than half of these have been allocated to SC/ST/ OBC entrepreneurs.
- About 68% of loan accounts have been given to women entrepreneurs.
Stand Up India Scheme

The Stand-Up India Scheme aims to promote entrepreneurship among the Scheduled Caste/ Scheduled Tribe and Women by facilitating bank loans of value between Rs. 10 lakh and Rs. 100 lakh to at least one SC/ ST borrower and one-woman borrower per bank branch of Scheduled Commercial Banks for setting up Greenfield enterprises in trading, manufacturing, services sectors & Activities allied to agriculture. In 2019-20, the Stand-Up India scheme was extended for the entire period coinciding with the 15th Finance Commission period of 2020-25.
PM Jan Dhan Yojana
PM Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) was launched as the National Mission for Financial Inclusion, with the aim to provide universal access to banking facilities with at least one basic bank account to every household. Key highlights, as of March 2025, include:
PM Jan Dhan Accounts: 55.17 crore
Deposit in accounts: Rs. 2,61,461.25 crore
Women accounts: 30.80 crore
PM SVANidhi
PM SVANidhi was launched with the aim to facilitate collateral free working capital loan to street vendors to restart their businesses, which were adversely impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic. As of March 31, 2025, 68 lakh street vendors got loans through PM SVANidhi.
PM Vishwakarma Scheme
Millions of artisans and craftsmen once faded into obscurity in a modernising economy. The PM Vishwakarma Yojana offers collateral-free loans, toolkits, digital incentives, and marketing support. With 2.37 million registered artisans and nearly 1 million receiving toolkit incentives, traditional skills are being recognised, rewarded, and revived.
Supporting Entrepreneurs and Workers
Building financial stability required support for entrepreneurship, job creation, and formalisation of unorganised labor. So, government focused on building long-term employment and ensuring worker welfare.
Start Up India
India has firmly established itself as the 3rd largest startup and Unicorn ecosystem in the world, with over 1.57 lakh certificates issued by Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) for recognition of startups as of December 31, 2024. The nation's entrepreneurial landscape is fueled by 118 unicorns. Startup India is a flagship initiative by the Government of India to foster innovation and create a thriving startup ecosystem. Its goal is to drive economic growth and generate large-scale employment opportunities.
eShram Portal
eShram portal was launched to create a National Data Base for unorganised workers. The eShram portal provides an access to social security schemes, and a platform for skill development and job matching to unorganized workers.
As of May 29, 2025, more than 30.86 crore unorganized workers have been registered on the eShram portal. 53.75% of these registrations are women.
Pradhan Mantri Shram Yogi Mandhan Scheme
PM-SYM was launched to provide assured monthly pension of Rs. 3000 to unorganized workers on attaining the age of 60 years. It is a voluntary and contributory pension scheme.
As on May 29, 2025, 51.35 lakh unorganised sector workers are registered for this scheme.
Lakhpati Didi Scheme
A Lakhpati Didi is a Self-Help Group member with an annual household income exceeding Rs. 1,00,000. The government actively backs this initiative, promoting diversified livelihood activities and fostering collaboration across sectors for strategic planning and implementation. So far, more than 10 crore women have become part of self-help groups, and the government has a resolve of making 3 crore women Lakhpati Didis.
Employees’ State Insurance Corporation (ESIC)
The ESIC provides a comprehensive social security net for workers, including Medical Benefits, Cash Benefits and Unemployment Allowance.
|
Particulars
|
2014
|
2025 (31.03.2025)
|
Growth in (%)
|
|
No. of Insured Persons
|
2.03 Crore
|
4.09 Crore
|
101
|
|
No. of beneficiaries
|
7.89 Crore
|
15.87 Crore
|
101
|
|
No. of employers
|
6.70 Lakh
|
24.45 Lakh
|
265
|
The employers' contribution has been reduced from 4.75% to 3.25% and the employees' contribution reduced from 1.75% to 0.75%.
Dignity and Protection for Transgenders and Persons with Disabilities
True inclusivity also means protection and dignity for the most marginalised—persons with disabilities and transgender individuals—ensuring their integration into society.
Scheme of Assistance to Persons with Disabilities for Purchase/Fitting of Aids/Appliances (ADIP)
Under the ADIP scheme, funds are released to various implementing agencies for distribution of assistive devices to persons with disabilities to promote their physical, social and psychological rehabilitation and enhancing their economic potential.
Under the scheme, 31.16 lakh persons with disabilities have been provided assistive devices and aids at a cost of Rs. 2415.85 crore during the last 11 years.
The important achievements under the scheme during the last 11 years are as follows:
- 10 Guinness World Records created during the organisation of AIDP camps.
- Since 2014, 18,000+ camps have been conducted, empowering over 31 lakh Divyangjan.
- Divyangjan benefitting from the number of recognised disabilities has been revised from 7 to 21.
Schemes for Transgender Persons
The Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Act, 2019 has been enacted for protection of rights of transgender people and their welfare, and provisions of the same came into force on January 10, 2020. The Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Rules, 2020 were formulated and published in Gazette of India on September 29, 2020.
Ministry has also launched a scheme SMILE - Support for Marginalized Individuals for Livelihood and Enterprise on February 12, 2022 which includes sub scheme - ‘Comprehensive Rehabilitation for Welfare of Transgender Persons’.
On August 21, 2020, National Council for Transgender Persons was constituted to advise Government on policies, programmes, legislation and projects with respect to transgender persons. The Ministry has launched National Portal for Transgender Persons on November 25, 2020. Any Transgender applicant can obtain Certificate of Identity and Identity Card without any physical interface with the office of issue.
Ministry has initiated 12 pilot shelter homes namely 'Garima Greh': Shelter Home for Transgender Persons. The main aim of these shelter homes is to provide safe and secure shelter to Transgender persons in need.
Bridging the Gap: Inclusive Growth for SCs, STs, OBCs & Minorities
Welfare must be anchored in social justice. The government expanded focus on Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, OBCs, and minorities, who had long been left behind in national progress.
- 60% of current union ministers are from the minority categories.
- More than four times Eklavaya Residential schools have been sanctioned since 2014 (From 123 in 2013-14 to 477 in 2024-25).
- 71% of the farmers covered by PM Fasal Bima Yojana are SC/ST/OBC.
- 80% small and marginal farmers, mostly SC/ST/OBC, are receiving income support under PM-KISAN.
- 44.19% of the houses under PMAY(G) are for SC/ST.
- 58% of the government scholarship recipients are SC/ST/OBC.
- A National Commission for De-notified, Nomadic and Semi-Nomadic Tribes (NCDNT) was constituted by Government of India in February 2014.
- Constitutional status granted to National Commission of Backward Classes in 2018 in the 102nd Constitutional Amendment.
Honouring Cultural Heritage and Tribal Legacy
Beyond schemes and statistics, cultural pride and recognition of historical contributions were essential. Janjatiya Gaurav Diwas embodies this spirit of respect and remembrance. Every year on November 15th, Janjatiya Gaurav Divas is celebrated to honor the contributions of these communities, especially in India’s freedom struggle. The day marks the birth anniversary of Bhagwan Birsa Munda, a tribal leader and freedom fighter, whose legacy continues to inspire. This occasion highlights the important role of tribal groups in preserving India’s heritage and advancing its progress.
Further, recognizing the contributions of social justice pioneers, the government redeveloped five iconic sites linked to Dr. B. R. Ambedkar as the Panchteerth, while also honouring the legacy of tribal heroes by sanctioning 11 Tribal Freedom Fighter Museums across 10 states.
Achieving 100% Saturation of Schemes and Inclusive Development
Viksit Bharat Sankalp Yatra
To ensure these initiatives reached every citizen, implementation mechanisms like the Viksit Bharat Sankalp Yatra were launched to track progress and improve last-mile delivery. The Viksit Bharat Sankalp Yatra is a government initiative being undertaken across the country, to raise awareness about and track the implementation of flagship central schemes. This Yatra has reached 2.6 lakh gram panchayats and more than 4,000 urban local bodies in the country and aims to achieve the target of taking public welfare schemes to 100% saturation.
Aspirational Districts Programme (ADP)
Parallel to monitoring, the Aspirational Districts Programme brought focused attention to India’s most backward regions, demonstrating the commitment to equitable development. The Aspirational Districts Programme (ADP) is a transformative initiative aimed at accelerating the development of 112 relatively backward and remote districts across India.
Since its inception, ADP has achieved several important results in improving development in some of India’s most underdeveloped areas. The biggest improvements have been seen in health, nutrition, and basic infrastructure like sanitation, electricity, and clean water, helped by schemes like Swachh Bharat and SAUBHAGYA.
By the end of 2019, in just a year of the beginning of the programme, 8 districts have moved from Tier IV to Tier I category. These districts belong to Bihar, Assam and Chhattisgarh.
Conclusion
As Bharat steps confidently toward its centenary of independence, the path to Viksit Bharat lies in the continued empowerment of its most vulnerable citizens. By ensuring last-mile delivery, nurturing human capital, and fostering dignity through inclusion, the government’s vision of Sabka Saath, Sabka Vikas, Sabka Vishwas, Sabka Prayas is not just a motto—it is a lived and measurable reality.
References
Department of Drinking Water & Sanitation
Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs
Department of Financial Services
Ministry of Finance
Department of Food & Public Distribution
Ministry of Labour and Employment
Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment
https://pmaymis.gov.in/
https://eshram.gov.in//dashboard
https://socialjustice.gov.in/schemes/37
https://maandhan.in/maandhan/summary
https://pmayg.nic.in/netiay/PBIDashboard/PMAYGDashboard.aspx
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2114280
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=1946307
https://mon.nic.in/scheme/saubhagya-sahaj-bijli-har-ghar-yojana/
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2114291
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2086486
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressNoteDetails.aspx?NoteId=154426
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2112459
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2118208
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressNoteDetails.aspx?NoteId=154355
https://www.pib.gov.in/Pressreleaseshare.aspx?PRID=1781643
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=2070639
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2114861
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2130161
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetailm.aspx?PRID=2093136
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=1806166
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2073246
https://www.pib.gov.in/FeaturesDeatils.aspx?NoteId=154503
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2124545
https://www.mospi.gov.in/sites/default/files/publication_reports/HCES%20FactSheet%202023-24.pdf
https://services.india.gov.in/service/detail/lakhpati-didi-yojana-by-ministry-of-rural-development-1
Click here to see in PDF
Explainer 08/ Series on 11 Years of Government
Santosh Kumar | Sheetal Angral | Rishita Aggarwal
(Explainer ID: 154590)
आगंतुक पटल : 7296
Provide suggestions / comments