Social Welfare
Bridging Gaps, Building Futures: 11 Years of Inclusive Growth for Minorities
Posted On:
23 JUN 2025 11:45AM
|
Key takeaways
1. National Minorities Development and Finance Corporation: Rs. 752.23 crore disbursed to over 1,74,148 beneficiaries (as of 10.03.25)
2. ₹3 Cr released in FY24 under Jiyo Parsi scheme, aiding birth of 400+ Parsi children since inception.
3. 2014-15 to 2024-25: ₹18,416 Cr worth projects approved under Pradhan Mantri Jan Vikas Karyakram
4. PM VIKAS merged 5 schemes, benefitting minority youth and women through skill and leadership training.
5. Waqf Amendment Act, 2025 introduced; UMEED Portal to digitize and reform management of Waqf properties.
|
Introduction
In the last eleven years, the Government of India has taken significant strides toward fostering inclusive development and bridging socio-economic gaps for the six centrally notified minority communities- Muslims, Christians, Sikhs, Buddhists, Parsis, and Jains. Through a blend of educational opportunities, economic empowerment schemes, community infrastructure projects, cultural preservation, and digital reforms, the groundwork has been laid for sustainable and equitable growth. These initiatives showcase a steadfast commitment to ensuring dignity, equal opportunity, and holistic development for all minority citizens of India.
Schemes supporting Minorities in India
Education
Maulana Azad National Fellowship (MANF): The scheme for minority students was launched in 2009-10 as a Central Sector Scheme. The objective of the scheme was to provide fellowships in the form of financial assistance to students belonging to the minority communities to pursue degrees in higher education such as M.Phil. and Ph.D. in India. The fellowship amount to the selected candidates was disbursed in Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) mode and credited directly into the account of the beneficiary. The Maulana Azad National Fellowship (MANF) scheme has been discontinued from 2022-23 due to its apparent overlapping with similar schemes of other Ministries.
Padho Pardesh: This Interest Subsidy Scheme aims to award interest subsidy on educational loan to minority students for studying abroad to pursue approved courses of study at Masters, M.Phil. and Ph.D. levels. The scheme has been discontinued from FY 2022-23 as education loan is available at cheaper rates through various other Government interventions.
Begum Hazrat Mahal National Scholarship: Scholarships were awarded to girls, from the minority communities, studying in classes IX to XII. The scheme was implemented by Maulana Azad Education Foundation (MAEF) – an autonomous body under Ministry of Minority Affairs (MoMA). Students whose parents’/ guardians’ annual income does not exceed Rs. 2.00 lakh are eligible for scholarship under the scheme.
Naya Savera: (‘Free Coaching and Allied’ scheme) was launched in 2007 to assist students/candidates belonging to the six notified minority communities namely Sikh, Jain, Muslim, Christian, Buddhist and Parsi by way of special coaching for qualifying examinations for admission in technical/professional courses and competitive examination for recruitment to Group ‘A’, ‘B’, & ‘C’ services and other equivalent posts under the Central and State Governments including public sector undertakings, banks and railways.
Employment and Economic Empowerment Schemes
The Pradhan Mantri Virasat Ka Samvardhan (PM VIKAS)
PM VIKAS is a flagship Scheme of the Ministry which converges five erstwhile schemes viz. ‘Seekho Aur Kamao’, ‘Nai Manzil’, ‘Nai Roshni’, ‘Hamari Dharohar’ and ‘USTTAD’; and focuses on upliftment of six notified minority communities through skill development; entrepreneurship and leadership of minority women; and education support for school dropouts.
- Seekho aur Kamao: Implemented for six notified minority communities to upgrade skills of youth (14–45 years) in modern/traditional trades based on qualifications, economic trends, and market potential for employment or self-employment. 33% of funds earmarked for women.
- Nai Manzil: Launched on 8th August 2015 with 50% World Bank funding, for minority school dropouts or those from Madarasas. It provided formal education (Class VIII/X) and skill training for better employment.
- Nai Roshni: Aimed to empower minority women (18–65 years) through a six-day non-residential/five-day residential training on women-centric topics like health, legal rights, financial/digital literacy, life skills, Swachh Bharat, and social advocacy.
- Humari Dharohar: A scheme to preserve the rich heritage of minority communities through exhibitions, literature/document preservation under Indian Culture. It does not include preservation of heritage buildings.
- USTTAD: Launched on 14th May 2015 to preserve traditional minority arts/crafts. Focuses on skill upgrading of artisans, documentation, standard setting, youth training by master craftsmen, and developing market linkages.

The scheme is intended to be implemented in convergence with the ‘Skill India Mission’ of Ministry of Skill Development & Entrepreneurship and through integration with the Skill India Portal (SIP).
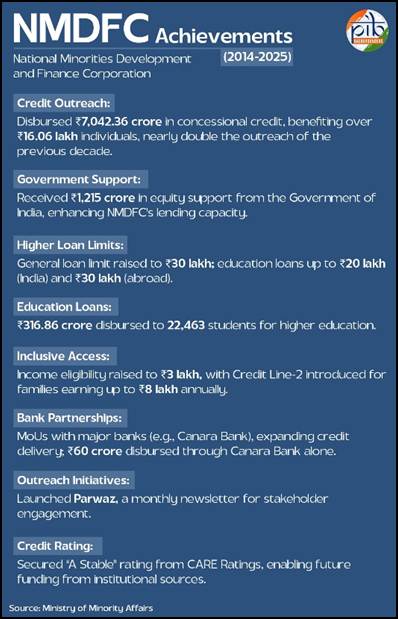
National Minorities Development and Finance Corporation (NMDFC)
Launch Date: NMDFC provides concessional loan to “Backward sections” amongst the notified minorities for self-employment income generation activities under its schemes of Term loan, Education loan, Virasat scheme & Micro Finance scheme through State Channelizing Agencies (SCAs) nominated by respective State Govt./ UT Administration and Canara Bank.
Objective: NMDFC provides concessional credit for self-employment and income generating activities for the socioeconomic development of the ‘backward sections’ amongst the notified Minorities.
Key Achievements:
- In 2014-15, Rs. 431.20 crore was disbursed
- NMDFC has disbursed Rs. 752.23 crore to over 1,74,148 beneficiaries till 10th March 2025.
Infrastructure
Pradhan Mantri Jan Vikas Karyakram (PMJVK)
A Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS), PMJVK is an area development programme under which community infrastructure and basic amenities are being created in the identified areas. The infrastructure built up under the scheme is for the benefit of all people living in the area.
Since FY 2023, PMJVK Scheme was fully digitized with online monitoring via a dedicated portal, enhancing transparency and efficiency. In FY 2023–24, MoMA sanctioned new projects under PMJVK to preserve minority cultures through innovative infrastructure initiatives.
Since FY 2014-15 to FY 2024-25, the Ministry has approved projects worth Rs. 18416.24 Crore comprising of approx. 5.63 lakhs Units in various sectors like Health, Education, Sports, Sanitation, Women & child development, Renewable energy with a Central Share of Rs.13150.10 Crore to States/UTs and CGOs under PMJVK.
The Pradhan Mantri Jan Vikas Karyakram (PMJVK) has been implemented to reduce socio-economic disparities. The areas covered under PMJVK are 1300 Minority Concentration Areas identified across 308 Districts of 32 States/UTs in the country which include 870 Minority Concentration Blocks (MCBs) and 321 Minority Concentration Towns (MCTs), and 109 Minority Concentration District Headquarters. These integrated initiatives work collectively to bridge gaps, promote the welfare of minority communities, and ensure their full inclusion and empowerment in India's broader development.
Special Schemes
Haj Pilgrimage
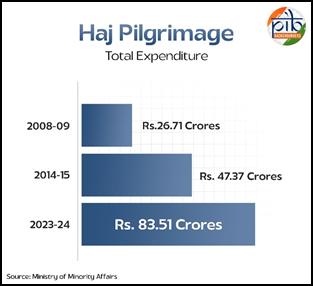
Launch Date: Haj pilgrimage including administration of the Haj Committee Act, 2002 and Rules made there under has been transferred from the Ministry of External Affairs to the Ministry of Minority Affairs from 1st October, 2016.
Objective: The Government of India recognizing the significance of Haj has made provisions to facilitate the pilgrimage, particularly for low-income individuals.
Key Achievements:
- 2014-15: Rs. 47.37 Crores Expenditure
- 2023-24: Rs. 83.51 Crores Expenditure
Initiatives taken for Haj Pilgrimage:
- Haj Suvidha App: The App was launched to leverage information technology for enhancing the pilgrimage experience. Pilgrims can use the app to access training content, accommodation and flight details, baggage information, an emergency helpline (SOS), grievance redressal, feedback, language translation, and miscellaneous information related to the pilgrimage. More information on the Haj Suvidha App.
- In April 2025, a two-day training for 620 Haj 2025 deputationists was held, urging them to serve pilgrims with sincerity and commitment.
- Haj Walkathon: Organized by the Delhi State Haj Committee, the event highlighted the importance of fitness for pilgrims preparing for the sacred Haj journey. The event was to emphasize the need for well-being and physical readiness of pilgrims ahead of their spiritual journey.
Buddhist Development Plan (BDP)
Aims to support the socio-economic advancement of the Buddhist population through infrastructure development in education, health, sports, renewable energy, and tourism. Projects include facilities for Buddhist schools, drinking water supply, and youth sports initiatives, mainly covering the Himalayan Belt, from Ladakh to Sikkim and parts of Delhi. Under this plan, projects worth ₹300.17 crore have been approved for Sikkim, Himachal Pradesh, Arunachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Ladakh, and institutions like Delhi University, CIHCS (Central Institute of Himalayan culture Studies) and CIBS (Central Institute of Buddhist Studies). These entities will serve as key implementing and supervising agencies, with a hub-and-spoke model centered around CIBS.
Qaumi Waqf Board Taraqqiati Scheme (QWBTS) and Shahari Waqf Sampatti Vikas Yojana (SWSVY)
These are schemes for automation and modernization of State Waqf Boards. Under QWBTS, Government Grants-in-Aid (GIA) is provided to State Waqf Boards through CWC for the deployment of manpower to computerize and digitize records of waqf properties and to enhance the administration of Waqf Boards. Under SWSVY, GIA is provided to CWC for further disbursement of interest-free loans to Waqf Boards / Waqf Institutions to develop commercially viable projects on waqf properties. Rs 23.87 crore and Rs 7.16 crore respectively were spent under QWBTS and SWSVY from 2019-20 to 2023-24.[19]
Jiyo Parsi Scheme
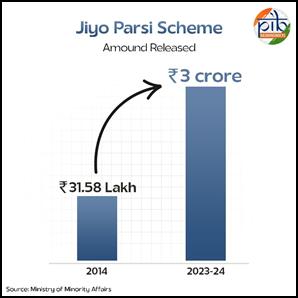
Launch Date: Jiyo Parsi is a unique Central Sector Scheme for arresting the population decline of the Parsi Community. The scheme was launched in 2013-14.
Objective: Unique Central Sector Scheme with an objective to reverse the declining trend of Parsi population by adopting scientific protocol and structured interventions to stabilize their population in India.
Key Achievements:
- In 2014-15, under the 'Jiyo Parsi' scheme, a total of Rs. 14,55,252 was allocated for medical assistance, while Rs. 17,03,500 was released for advocacy and outreach programs.
- For the financial year 2023-24, the scheme's Amount released to 3 Crores.
- For 2024-25, Rs. 6 crores (BE) has been allotted.
- Since its inception, the scheme has contributed to the birth of over 400 Parsi children, as of 31st March 2024.
Creating History: Waqf Amendment Act, 2025
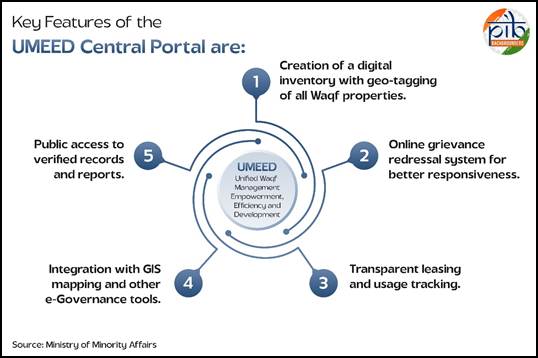
The Waqf (Amendment) Act, 2025, which was notified on 08/04/2025 aims to fix problems in the management and governance of Waqf properties. The Amendment Act marks a significant step towards modernizing the management of waqf properties in India. It brings stronger legal provisions for transparency and accountability, and adoption of digital tools for efficient asset auditing and oversight. These reforms aim to protect waqf assets from misuse, ensure they serve their intended religious and charitable purposes, and empower the Muslim community through improved governance aligned with global best practices. The Waqf (Amendment) Act, 2025 aims to update the Waqf Act, 1995, to solve problems in managing Waqf properties.
On 6th June 2025, the Ministry of Minority Affairs launched the UMEED Central Portal, a centralized digital platform for real-time uploading, verification, and monitoring of Waqf properties. The UMEED Central Portal, short for Unified Waqf Management, Empowerment, Efficiency and Development Act, 1995 will serve as a centralized digital platform for real-time uploading, verification, and monitoring of Waqf properties. The portal is expected to bring about a paradigm shift in how Waqf assets are administered across India by introducing greater transparency, accountability, and public participation.
Amplifying Efforts

The Ministry of Minority Affairs organises 'Lok Samvardhan Parv', bringing together minority artisans from across India.
The platform offers artisans a unique opportunity to showcase their indigenous arts, crafts, and rich cultural heritage. The event has been designed not only to promote the traditions of minority communities but also to foster an innovative and entrepreneurial environment for artisans.
To enhance their skills in areas like marketing, export & online business, design, GST and sales etc., workshops are conducted by the Ministry, with support from the Export Promotion Council for Handicrafts (EPCH), ensuring a holistic approach to empowering their talent. So far, the Ministry has organised 3 Lok Samvardhan Parvs, as under:
- July, 2024 at Dilli Haat, INA, New Delhi
- January, 2025 at Baba Kharak Singh Marg, New Delhi
- April, 2025 at Convocation Ground, Kashmir University, Srinagar, Jammu & Kashmir
Additionally, the following initiatives have been undertaken:
- The Ministry, in collaboration with DSGMC (Delhi Sikh Gurdwara Management Committee), approved ₹25 Cr in-principle for a Centre of Gurumukhi Script at Khalsa College, Delhi University, to preserve Sikh linguistic and cultural heritage.
- ₹11.17 Cr was sanctioned for the Centre for Avesta Pahlavi Studies at Mumbai University to preserve Parsi heritage.
- Two MoUs were signed with Mumbai University for a ₹11.17 Cr Avesta Pahlavi project and with CIHCS (Central Institute of Himalayan Culture Studies) for ₹40 Cr infrastructure development.
- Ministry has given in-principle approval for two projects for the Jain community - a Centre for Jain Studies at DAVV, Indore, and a Centre of Jain Manuscriptology at Gujarat University, with a total estimated cost of ₹65 Cr.
Conclusion:
Over the past 11 years, the Government of India has made significant strides in uplifting minority communities through targeted educational, economic, and infrastructure programs. With dedicated schemes and specialized initiatives for unique needs, including scholarship support, digital reforms, and heritage preservation, the Ministry of Minority Affairs has fostered greater inclusion and empowerment. Recent legislative amendments and digitalization efforts, such as the UMEED portal, further strengthen transparency and efficiency in governance. Collectively, these sustained efforts reflect a strong national commitment to promoting equal opportunity, celebrating diversity, and ensuring that minority communities play an active role in India’s ongoing development.
References:
The Ministry of Minority Affairs:
The Ministry of External Affairs:
Click here to see in PDF
Explainer 22/ Series on 11 Years of Government
Santosh Kumar/ Ritu Kataria/ Kritika Rane
(Explainer ID: 154720)
आगंतुक पटल : 3704
Provide suggestions / comments