Social Welfare
A Decade of Building Skills & Empowering Dreams
10 years of Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana
Posted On:
14 JUL 2025 11:16AM
Key Takeaways
- Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship has empowered over 6 crore Indians through its various schemes since 2014.
- Over 1.6 crore youth trained nationwide since 2015 under PMKVY.
- Courses expanded to emerging fields like AI, Robotics, and IoT.
- As of July 11, 2025, over 25 lakh candidates have been trained under PMKVY 4.0.
|
Introduction
India’s growing youth population holds immense potential, but harnessing this demographic dividend requires the right skills. Through focused efforts in skilling, apprenticeships, entrepreneurship, global workforce readiness, and promotion of traditional trades, the government is empowering its citizens to become drivers of economic and social progress. Since 2014, the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship has empowered more than 6 crore Indians through its various schemes to build a brighter future for themselves and for the country.
At the heart of this transformation is India’s Skill India Mission (SIM), which is equipping youth with essential industry-relevant skills through various programs. These initiatives focus on skill development, re-skilling and up-skilling, empowering millions with the tools needed for sustainable careers. By bridging the skill gap, fostering innovation, and creating new job opportunities, SIM is paving the way for a self-reliant and developed India (Atmanirbhar and Viksit Bharat).
SKILL INDIA MISSION
The Skill India Mission (SIM) delivers skill, re-skill and up-skill training through an extensive network of skill development centres / institutes under various schemes. In February 2025, the restructured ‘Skill India Programme’ was approved for 2022-23 to 2025-26, merging Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana 4.0 (PMKVY 4.0), the Pradhan Mantri National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme (PM-NAPS), and the Jan Shikshan Sansthan (JSS) Scheme into a single Central Sector Scheme.
- Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY)- Provides short-term skill training and upskilling/re-skilling through Recognition of Prior Learning (RPL) to youth nationwide, including rural areas.
- Jan Sikhshan Sansthan (JSS)- Offers vocational skills to non-literates, neo-literates, and school dropouts (up to 12th standard), aged 15–45. Focuses on women, SC, ST, OBC and minorities in rural and low-income urban areas. More than 26 lakh people have been trained from FY 2018-19 to FY 2023-24 under the scheme.
- National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme (NAPS)- Promotes apprenticeship by offering financial support for apprentice stipends. Training includes both basic and on-the-job/practical training in industries. Under PM-NAPS, over 43.47 lakh apprentices have been engaged across 36 States and Union Territories as of 19 May 2025, with participation from more than 51,000 establishments.
In order to create an adaptive and responsive skill development ecosystem, two new Centres of Excellence were announced at National Skill Training Institutes (NSTIs) in Hyderabad and Chennai on June 16, 2025. These centres will serve as national reference points for high-quality instructor training and specialised skilling aligned with emerging domains.
|
Transforming Futures: PMKVY Marks a Decade of Skill Development
The Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY) scheme was launched on July 15, 2015 to encourage and promote skill development in the country by providing free short duration skill training and incentivizing this by providing monetary rewards to youth for skill certification.
The aim of the scheme is to boost both industry and employability of youths. After the successful implementation of pilot PMKVY (2015-16), PMKVY 2016-20 was launched by scaling up both in terms of sector and geography and by greater alignment with other missions of Government of India like Make in India, Digital India, Swachh Bharat, etc.


Under the Scheme, every certified candidate is given a reward of Rs. 500 for clearing the exam as encouragement.
Placements were tracked under Short Term Training (STT) component of PMKVY in the first three versions of the scheme which is PMKVY 1.0, PMKVY 2.0 and PMKVY 3.0 implemented from FY 2015-16 to FY 2021-22. The reported placement rate in STT certified candidates till PMKVY 3.0 was 42.8%.
Under PMKVY 4.0, the focus is to empower trained candidates to choose their varied career path and they are suitably oriented for the same. To enable the opportunities for employments, Skill India Digital Hub (SIDH) platform has been launched to integrate skilling, education, employment, and entrepreneurship ecosystems.

Empowering Youth, Powering the Nation
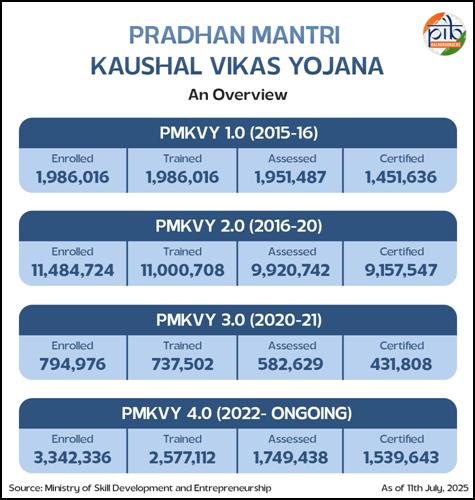
PMKVY 1.0: During its pilot phase in 2015-16, 19.85 lakh candidates were trained.
PMKVY 2.0: 1.10 Crore candidates were trained/oriented.
PMKVY 3.0: Two special programs under were launched:
- Customised Crash Course Programme for COVID Warriors (CCCP for CW) to mitigate the impact of COVID-19 pandemic
- Skill Hub Initiative (SHI) for integration and mainstreaming of vocational education with general education as envisaged under the National Education Policy, 2020 (NEP, 2020).
- Under PMKVY 3.0, 7.37 lakh candidates were trained, including 1.20 lakh candidates under CCCP-CW and 1.8 lakh under SHI.
PMKVY 4.0: Under PMKVY 4.0, during the last three financial years (2022–23, 2023–24, 2024–25) - as on 31.12.2024), Rs. 1244.52 crore has been utilized across States/UTs. As of July 11, 2025, over 25 lakh candidates have been trained under this phase.
Over the years, more than 1.63 crore candidates have been trained under PMKVY in diverse sectors, such as, manufacturing, construction, healthcare, IT, electronics, retail and more.
National Skilling Through PMKVY
Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY) became the foundation of India’s short-term skilling ecosystem. It aims to equip youth from all walks of life with practical, job-ready skills through a structured, quality-assured training and certification system. Over the years, candidates have been trained under PMKVY in diverse sectors, such as, manufacturing, construction, healthcare, IT, electronics, retail and more.
Through PMKVY, certified skills training reached even rural and remote areas of the country, democratizing access to employability opportunities. Inclusivity was a key pillar of the scheme with 45% of the candidates being women and a significant share coming from Scheduled Castes (SCs), Scheduled Tribes (STs), and Other Backward Classes (OBCs). Over time, PMKVY evolved to address demands of the future economy, expanding its scope to include cutting-edge sectors like Artificial Intelligence, Drone Technology, Robotics, Mechatronics and Internet of Things (IoT).
Innovative initiatives by PMKVY:
- Special Projects: Targeted skilling for marginalized groups included training 2,500 Bru-tribe candidates in Tripura, jail inmates in Assam and Manipur, and 13,834 (70% women) under the PANKH project across 18 states.
- Traditional Crafts & Upskilling: Under PMKVY 3.0, 2,243 women were trained in Jammu & Kashmir’s Namda craft. An RPL upskilling project for artisans and weavers in Nagaland and J&K trained 9,605 candidates. Both projects were led by the Handicraft and Carpet Sector Skill Council.
- Mainstreaming Skilling: PMKVY supports flagship government initiatives (e.g., PM Surya Ghar, Vibrant Villages Programme, Beti Bachao Beti Padhao, Jal Jeevan Mission, Green Hydrogen Mission), embedding skill development into these schemes for broad impact.
- COVID-19 Response: Over 1.2 lakh health workers were trained through a Customized Crash Course Programme for COVID Warriors.
- Skill Hub Initiative: Over 1.23 lakh youth trained using schools and colleges as vocational hubs, aligning with NEP 2020 (National Education Policy).
- Recognition of Prior Learning (RPL): Informal workers’ skills are formally recognized, boosting employability without lengthy training.
- Digital & Outcome-Driven Reforms: The Skill India Digital Hub (SIDH) tracks training digitally, ensures Aadhaar-based validation, and links payments to performance.
- Academic Mobility: PMKVY 4.0 integrates skill qualifications with the Academic Bank of Credits (ABC), enabling transfer of credits between skill and formal education.
Other Schemes Empowering Skill Development
PM Vishwakarma Yojana
The Scheme, launched on 17th September, 2023 aims to provide end-to-end support to artisans and craftspeople of 18 trades who work with their hands and tools. The Scheme components include recognition through PM Vishwakarma Certificate and ID Card, Skill Upgradation, Toolkit Incentive, Credit Support, Incentive for Digital Transactions and Marketing Support. PM Vishwakarma will be implemented as a Central Sector Scheme, fully funded by the Government of India, with an initial outlay of Rs 13,000 crore and is set to run for five years, until 2027-28.
As of July 13, 2025, more than 2.7 crore applications have been submitted under the PM Vishwakarma Yojana, with more than 29 lakh applications successfully registered.
Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Grameen Kaushalya Yojana (DDU-GKY)
Launched on 25th September 2014, DDU-GKY is a part of the National Rural Livelihood Mission (NRLM), tasked with the dual objectives of adding diversity to the incomes of rural poor families and cater to the career aspirations of rural youth.
Under the scheme, 65% of the candidates have been placed in gainful employment after completing their training. From FY 2014-15 a total of 16,90,046 candidates have been trained and 10,97,265 candidates have been placed till November, 2024.
Rural Self Employment and Training Institutes (RSETIs)
Launched in January 2009, the scheme envisages framework for imparting good quality residential free training and post training follow up with credit linkage for sustained motivation among the trainees for promoting entrepreneurship among the rural youth. As RSETIs are Bank lead institutions they are prefixed with the name of the respective sponsor banks to give distinct identity.
As of June 30, 2025, a total of 56,69,369 candidates have been trained in the 2025-26 financial year, compared to 22,89,739 candidates trained in the 2016-17 financial year.
Conclusion
The Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY) has evolved into much more than a government programme, it embodies India’s commitment to empowering its youth through skill development and lifelong learning. By fostering inclusion, embracing innovation, and demonstrating resilience in the face of change, the scheme is equipping millions with the tools and confidence needed to thrive in a rapidly transforming world. As India advances towards a knowledge-driven economy, PMKVY remains a cornerstone in shaping a skilled, entrepreneurial, and globally competitive workforce, ensuring that the nation’s demographic dividend is fully realized.
References:
Ministry of Skill Development
· https://www.skillindiadigital.gov.in/pmkvy-dashboard
· https://www.msde.gov.in/offerings/schemes-and-services/details/pradhan-mantri-kaushal-vikas-yojana-2-0-pmkvy-2-0-2016-20-AzM3ETMtQWa
· https://www.msde.gov.in/media/gallerydetail/digital-launch-of-pradhan-mantri-kaushal-vikas-yojana-3-0-pmkvy-3-0-2020-21-QjM3YTMtQWa
· https://sansad.in/getFile/loksabhaquestions/annex/179/AU2410.pdf?source=pqals
· https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=2003662
· https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2034984
· https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2115272
· https://www.skillindiadigital.gov.in/home-dashboard/jss-dashboard
· https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2131391
· https://pmvishwakarma.gov.in/
· https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2098551
Ministry of Rural Development: https://dashboard.rural.nic.in/dashboardnew/rseti.aspx
Download in PDF
***
RT/M
(Explainer ID: 154880)
आगंतुक पटल : 11366
Provide suggestions / comments