PIB Headquarters
Export Surge: India Steps Up on Global Stage
Exports surged by 5.19% in April-August 2025 vs. April-August 2024, boosting trade confidence
Posted On:
07 OCT 2025 1:23PM by PIB Delhi
- In August 2025, Indian exports registered a positive growth of 4.77% vs. August 2024.
- Exports increased by 5.19% to USD 346.10 billion in April-August 2025 in comparison to April-August 2024.
- Merchandise export rose by 2.31% and service export up surged by 8.65% in April-August 2025.
- India’s exports to Hong Kong, China, USA, Germany, Korea, UAE, Nepal, Belgium, Bangladesh, and Brazil have climbed the ladder of growth in April-August 2025 vs. April-August 2024.
|
|
Introduction
The journey of Indian exports is a result of innovation with global integration. Starting from the Silk Route to post-liberalisation boom, exports have been diversified from spices and textiles to technology, pharmaceutical, and engineering goods. According to World Bank Data, the world’s export is growing at 2.5%, whereas India’s export is growing at 7.1% (2024) outpacing global growth, and indicating the progress of the country on the international front. The share of exports in Indian GDP has increased from 19.8% in 2015 to 21.2% in 2024, which also indicates the growing relevance of exports in the Indian economy (World Bank). India’s trade performance continued its trend of growth in the first five months of FY 2025–26 too.
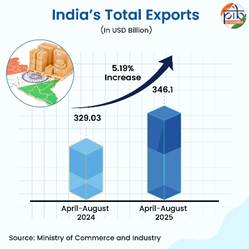
- 5.19% growth in total exports (merchandise and service exports combined) in April-August 2025 vs. April-August 2024
- Total export value for April–August 2025 stood at USD 346.10 billion, compared to USD 329.03 billion in April-August 2024
- The share of merchandise exports in April-August 2025 was 53.09%
- Service exports accounted for 46.91% in April-August 2025
- 4.77% growth in exports experienced in August 2025 vs. August 2024
Acknowledging this growth trajectory, the government has also set a target of USD 1 trillion of exports in the current financial year 2025-26 out of which 34.61% has already been achieved in the first five months.
Catalysed by government reforms, digital transformation, and entrepreneurial spirit, India’s export sector stands at the cusp of new possibilities, capturing the world’s attention and reshaping the story of Atmanirbhar Bharat on the global stage.
Unveiling Key Drivers Behind Merchandise Export Growth
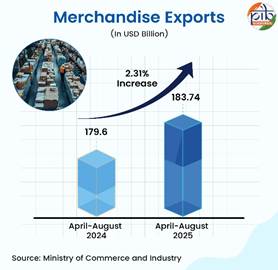
India’s merchandise export is on an upward trajectory in 2025. It registered healthy growth of 2.31% in April-August 2025 where exports were USD 183.74 billion as compared to USD 179.60 billion during April-August 2024.
However, out of five months, 19% of the merchandise exports were done in August 2025 only, with 6.65% rise from last year.
India’s non-petroleum and non-gems & jewellery exports raised to USD 146.70 billion in April–August 2025 from USD 136.13 billion a year earlier, reflecting strong growth of 7.76%. This category highlights India’s export strength driven by engineering goods, electronics, pharmaceuticals, chemicals and others.
Commodities such as electronic goods, tea, mica & coal, textiles etc., registered impressive growth in April-August 2025 compared to last year.
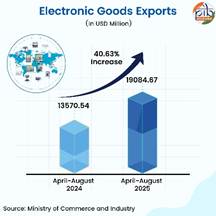
Electronic Goods
Electronic goods led the growth momentum, with exports rising by USD 5.51 billion, which is 40.63% rise in April-August 2025 compared to the prior corresponding period. The commodity excelled in August 2025 as well, with 25.91% growth in comparison to last year. In the last 10 years, production of electronic goods increased 6x and export of electronic goods increased 8x. Indian electronic goods exports are rising, with major markets including the USA, UAE, China, Netherlands and UK, driven by Make in India and PLI schemes.
Smartphones remain one of the key growth drivers, with India transforming from a net importer to a net exporter. Smartphone exports have crossed INR 1 lakh crore within just five months of FY26, which is 55% higher than the same period in the last fiscal.
Other Cereals
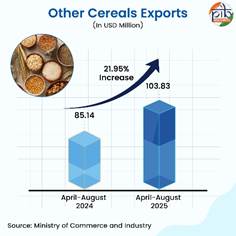
India’s exports of other cereals grew by 21.95% in April–August 2025 in comparison to April-August 2024. This includes Rye, Barley, Oats, Fonio, Quinoa, etc, and excludes Wheat, Rice, Maize, and Millet. One of the reasons behind the rise in global demand for other cereals is the awareness towards nutritious and health-conscious food products. With India’s rich agricultural heritage, these cereals add to agricultural diversity, enhancing food security and providing new export opportunities. Top export destinations are Nepal, Sri Lanka, UAE, Bangladesh, and Bhutan.
Meat, dairy and poultry products
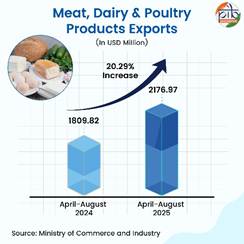
Meat, dairy, and poultry products experienced 20.29% growth in April-August 2025 when compared to the previous year. 17.69% rise was also noted during August 2025 in comparison to August 2024. Vietnam, UAE, Egypt, Malaysia and Saudi Arabia are some of the importers of Indian meat, dairy, and poultry products.
The rise in exports has been catalysed by various government initiatives. For instance, Agriculture Export Policy offers an institutional mechanism for pursuing market access and provides benefits to farmers to avail export opportunities. Agricultural and Processed Foods Export Promotion Scheme (APEDA) assists businesses in export infrastructure development, quality development and market development.
Tea
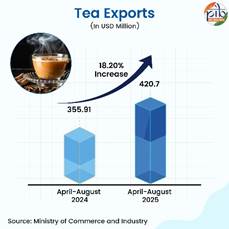
Tea registered export growth and reached 18.20% in April-August 2025 in comparison to last year. Tea exports also recorded a 20.50% rise in August 2025 compared to August 2024, adding momentum to overall tea export growth.
India achieved a significant milestone in the global tea industry, surpassing Sri Lanka to become the world’s second-largest exporter of tea in 2024. India’s Assam, Darjeeling, and Nilgiri teas rank among the world’s finest. Black tea leads the country’s exports, making up 96% of shipments, while varieties like green, herbal, masala, and lemon tea further enhance India’s global reputation.
India exports tea to several countries, with the UAE, Iraq, USA, Russian Federation, and Iran emerging as top destinations.
Mica, coal & other ores, minerals including processed minerals
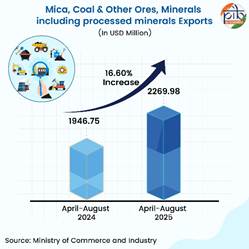
Mica, Coal & Other Ores, Minerals including Processed Minerals exports rose by 16.60% in April-August 2025 in comparison to last year. The increasing demand of the commodity was also experienced in August-2025, with a growth of 24.57% exports in comparison to last year. Some of the top countries where India exports processed minerals and their sub-products are China, USA, UK, Oman and Bangladesh.
Other Significant Commodities/Sectors
|
% Change in April-August 2025 vs. April-August 2024
|
|
Engineering goods
|
Drugs and pharmaceuticals
|
Readymade garments of all Textiles
|
|
 5.86% 5.86%
|
 7.30% 7.30%
|
 5.78% 5.78%
|
Engineering goods, India’s traditional export mainstay, also posted steady gains, climbing from USD 46.52 billion in April-August 2024 to USD 49.24 billion in April-August 2025 with 5.86% rise. The US remained the leading destination, alongside UAE, Germany, UK and Saudi Arabia. The key goods exported under the industrial machinery category are IC (Internal combustion) engines and parts, industrial machinery for dairy, food processing, textiles, industrial machinery like boilers, parts, machinery for injecting molding, valves, and ATMs. The Indian government has introduced numerous schemes to keep the export of engineering good robust such as Zero Duty Export Promotion Capital Goods (EPCG) and Market Access Initiative (MAI). These initiatives are aimed at encouraging the exporter and to help increase revenue from international markets.
Drugs and pharmaceuticals grew from USD 11.89 billion in April-August 2024 to USD 12.76 billion in April-August 2025, an increase of USD 0.87 billion (7.30%) over the year. India’s ability to supply affordable generics and specialty drugs sustained demand from advanced as well as emerging markets, with the USA, UK, Brazil, France, and South Africa featuring as the top buyers. Government initiatives for quality control and export promotion in this sector that evidently contribute to the growth include Uniform Code for Pharmaceutical Marketing Practices (UCPMP) 2024 and National Medical Devices Policy, 2023.
India is the 6th largest exporter of Textiles & Apparel globally, with a 4.1% share in CY24. Readymade garments of all textiles, a labor-intensive sector, continue to contribute positively. Exports rose to USD 6.77 billion with 5.78% increase in April-August 2025 compared to last year. Demand remained buoyant in traditional markets, led by the USA, UK, UAE, Germany, Netherland and Spain, reaffirming India’s strong presence in global apparel supply chains. The focus on Aatmanirbharta in the sector by boosting domestic value addition, advancing sustainable practices and strengthening India’s brand as a supplier of high-quality textile continues to accelerate the sector’s growth.
India’s Strategic Trade Ties: Top Merchandise Export Destinations
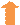
India’s strategic trade ties reflect its growing role in the global economy, with merchandise exports steadily expanding across diverse regions. India’s merchandise exports to several countries have increased in April-August 2025 in comparison to April-August 2024.
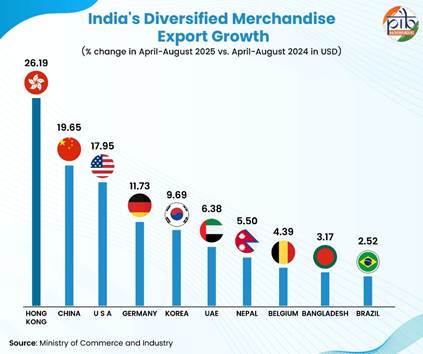
Hong Kong as a gateway: India’s merchandise exports to Hong Kong stood at ~USD 6.07 billion in 2024-25. These exports highlight India’s diverse trade portfolio, ranging from luxury items like gems and jewellery to engineering and electronic goods. The merchandise exports to Hong Kong in April-August 2025 rose by 26.19% to USD 2.62 billion. Hong Kong, long seen as a “Gateway to China,” now holds potential to become a “Gateway to India” amid rising India-China economic engagement. Re-export trade between India and China, through Hong Kong amounted to HK$97.9 billion (USD 12.59 billion) in 2024. This reflects India’s growing role in global trade and the strength of its export sectors.
Trade with Asian neighbour, China: India’s merchandise exports to China has witnessed a significant rise in recent years, reaching about $14.25 billion in FY 2024-25, with a strong 19.65% year-on-year increase in the April-August 2025. Key export commodities from India to China include petroleum products, engineering goods, electronic goods, organic and inorganic chemical products and iron ore and marine products. This reflects India’s expanding industrial capabilities and its role as a supplier of raw materials and intermediate goods to China’s manufacturing sector.
India’s export to the USA: India’s merchandise export to USA was USD 6.87 billion in August 2025. Mostly, the commodities India exports to USA are electronic goods, engineering goods, drugs & pharmaceuticals, gems & jewellery and textiles.
|
India’s Merchandise Export to USA vs. other countries
|
|
India’s export destinations
|
July 2025 (In USD million)
|
August 2025 (In USD million)
|
|
USA
|
8012.45
|
6865.47 ↓
|
|
UAE
|
2984.66
|
3245.26 ↑
|
|
Netherlands
|
1668.92
|
1829.77 ↑
|
|
Australia
|
495.65
|
554.67 ↑
|
|
Nepal
|
600.85
|
617.26 ↑
|
|
South Africa
|
611.28
|
654.58 ↑
|
|
Hong Kong
|
548.15
|
584.70 ↑
|
The consistent exports to the USA reflect India's rising competitiveness on the global stage and its ability to deliver high-value products to a dynamic market. This shows India’s preparedness in the situation of additional tariffs imposed by USA on Indian imports. There has been a decrease in export to the USA from July 2025 to August 2025 and increase in export with other countries in the same duration. While focusing on diversification, India is upgrading product quality, aligning with global standards, strengthening supply chains, and tapping new markets. Alongside rising exports, the country is diversifying its export destinations, boosting the global future of Indian products.
Trade with a European Country, Germany: India's merchandise export to Germany in 2024-25 was valued at approximately USD 10.63 billion. The key export items include engineering goods which is 40% of total exports, electrical and electronic equipment, organic and inorganic chemicals, Indian textiles and drugs & pharmaceuticals. In April-August 2025, Indian merchandise exports to Germany grew at 11.73% in comparison to last year, indicating growing business with the European country. India’s merchandise exports to Germany are vital as they deepen trade with Europe’s largest economy and a key hub for the EU market.
India’s presence in East Asia, Korea: India is one of Korea’s top trading partners with trade relations encompassing various sectors of the economy. In FY 2024-25, engineering goods (more than 40% of total exports to Korea), Petroleum products and Organic and Inorganic chemical took over 70% of the exports to Korea.In April-August 2025, the merchandise exports to Korea rose by 9.69 %, i.e., USD 2.63 billion in comparison to last year indicating the trust of Korea’s consumers on Indian products. These exports are further supported by the India-Korea Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA), which has reduced tariffs and improved market access for Indian businesses.
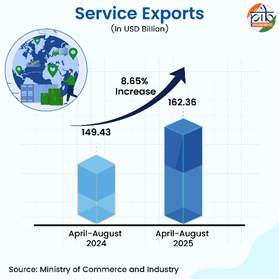
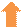
Services Exports: The New Engine of India's Export Growth
The services sector was referred as ‘Old War Horse’ in the Economic Survey 2024-25 which showcases its consistent strength and its role in driving the economy. In April-August 2025, with 8.65 % growth in comparison of last year, India’s services exports continued to demonstrate resilience and growth, reinforcing the country’s position as a leading player in the global services economy.
Driven by strong performances in sectors such as information technology, business process management, financial services, tourism, and professional consulting, the services segment remains a vital contributor to India’s foreign exchange earnings. The service sector had a trade surplus of USD 79.97 Billion in April-August 2025. Pertaining to this, service sector also contributes to the decline in the overall trade deficit with trade surplus in service sector. The increase in India's service exports in 2025 can be attributed to multiple key factors driving sustained growth:
Technology sector: India tech sector was 7.3% of total GDP in FY 2024. By 2030, India's digital economy is projected to contribute to nearly one-fifth of the country's overall economy. Technological advancements and the rapid adoption of digital solutions, including cloud computing, AI, and finTech, has expanded India's global competitiveness in high-value digital services. Schemes such as Digital India, Make in India and Startup India are also supporting the sector.
Demographic division: India has the largest youth population in the world, with about 65% of its people under the age of 35 which strengthens its competitive advantage over other countries. A young population represents a larger workforce with the potential for improved productivity and increased consumer demand. With the current demographic division and focus of India’s government on skill development with programs such as Skill India Program, the service sector keeps getting fuelled with skilled workforce.
Liberalisation of FDI Norms: The Government of India always strives to attract more FDI by removing regulatory barriers, streamlining processes, developing infrastructure, bettering logistics and improving the business environment by enhancing the Ease of Doing Business (EoDB). One of the examples is that the Union Budget 2025 announced the increase of FDI sectoral cap for the insurance sector from 74% to 100%. This enhanced limit is available for those companies, which invest the entire premium in India.
Similarly, in India-UK CETA, India has secured wide-ranging commitments from the UK. The UK commitments in digitally delivered services will enable continued robust growth in IT and Business Services to expand share in around 200 billion USD imports of UK. The continuous efforts of government for trade deals with countries and policies for the development in service sector results in study growth of the sector.
Government's Initiatives to Boost India's Export Competitiveness
India's export promotion schemes are a comprehensive set of government initiatives designed to boost export performance by addressing infrastructural inefficiencies, lowering costs, quality control and enhancing competitiveness. The result of these initiatives is that the rate of rejection of Indian exported products by importing countries reduced by 12.5% in June 2025 compared to June 2024.
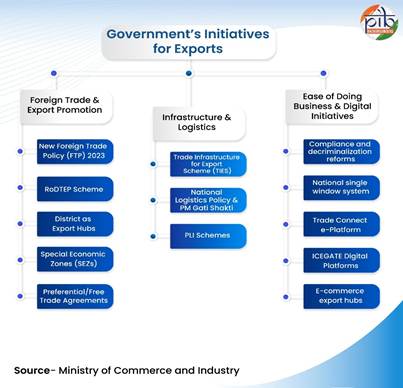
|
India is promoting foreign trade and exports through the Foreign Trade Policy 2023, which supports incentive to remission, ease of doing business, collaboration, and new markets. This also gives exporters the chance to close the old pending authorizations and start afresh. The RoDTEP scheme reimburses exporters for embedded duties, taxes, and levies that are not otherwise refunded under any other existing scheme. It has reimbursed nearly ₹58,000 crore as of March, 2025.
Initiatives like Districts as Export Hubs are making states and districts active players in trade. 734 districts have been identified with export potential with District Export Action Plans (DEAP) prepared for 590 districts. Supporting the trade, SEZs are also boosting jobs, investment, and exports worth ₹14.56 lakh crore in FY 2024-25, marking 7.37% growth in comparison to last year.
|
|
India is improving its trade and logistics through several key initiatives. The TIES (Trade Infrastructure for Export Scheme) help build export-focused infrastructure like testing labs, warehouses, and cargo facilities. The PM GatiShakti plan and National Logistics Policy are making transport faster, greener through multi-modal connectivity across transport and infrastructure sectors, with India’s global logistics rank rising to 38 in 2023 from 44 in 2018. Meanwhile, the PLI scheme, launched in 2020 is boosting manufacturing across 14 sectors, attracting ₹1.76 lakh crore investments, generating ₹16.5 lakh crore in output, and creating over 12 lakh jobs by March 2025.
|
|
India has taken big steps in ease of doing business, moving up from rank 142 in 2014 to 63 in 2020. Major contributors are reforms like scrapping 42,000 compliances and decriminalizing over 3700 legal provisions since 2014.
Digital tools are also transforming the trade. The National Single Window System simplifies approvals, Trade Connect e-Platform guides exporters for addressing trade queries and enhancing access to international markets, E-Commerce Export Hubs provide integrated facilities like customs, certification, packaging, and warehousing, linking smaller cities to global markets, and ICEGATE streamlines e-filing, e-payments, on-line registration for IPR, document tracking status at Customs EDI, online verification and others. It is a 24x7 helpline facility.
|
New Moves to Take India Global
Next-Generation GST Reforms
- 90% provisional refund for zero-rated supplies based on system-driven risk checks from November 1, 2025.
- Removes value-based threshold limit for GST refund on exports. This will support small exporters as they can claim refunds on their small value consignments too.
- GST cuts on paper packaging, textiles, leather, and wood from 12–18% to 5% resulting in lower production costs, enabling exporters to offer more competitive prices. GST on trucks and delivery vans, reduced from 28% to 18%, and lower GST on packaging materials reducing freight and logistics costs, enhancing competitiveness. Besides, GST on toys and sports goods have been cut from 12% to 5%, incentivising domestic production, countering cheap imports, and tapping rising global demand.
- The place of supply for “intermediary services” will be determined as per the location of the recipient of such services, to help Indian exporters of such services claim export benefits.
- Correction of inverted duty structures in textiles and food processing eases working capital pressure, reduces refund dependency and encourages domestic manufacturing.
- 90% provisional refunds for inverted duty structure (IDS) claims on a risk-based basis.
Export Promotion Mission
The Export Promotion Mission, announced in the Union Budget 2025-26, is being coordinated by the Department of Commerce along with the Ministry of MSME and Ministry of Finance. Under the mission, ₹2,250 crore initiative has been proposed with the intent to address challenges related to export credit accessibility, factoring for cross-border trade, and overcoming non-tariff barriers, with a particular focus on supporting MSMEs.
New Trade Agreements
Trade agreements are agreements between the country(s) or regional blocks to reduce or eliminate trade barriers, though mutual negotiations with a view to enhancing trade. Some of the new trade agreements which are being discussed or are released are:
● India-UK Comprehensive Economic and Trade Agreement (CETA)
● India-EU Free Trade Agreement
● India-Australia Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement
● India-New Zealand Free Trade Agreement
● India and Oman Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA)
● India- Peru Free Trade Agreement (FTA)
● India- Chile Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA)
- India- UAE Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA)
Conclusion
India’s robust export performance spanning both merchandise and services, shows the nation’s growing competitiveness and resilience in the global market. The significant growth in top-performing commodities such as electronics goods, other cereals, tea, dairy, mica products, combined with increased merchandise exports to key destination countries, highlights the effectiveness of India's export initiatives and schemes. The government’s policy interventions have provided a confidence boost to exporters, supported innovation, eased the market for business and expanded market opportunities. As Indian trade standards continue to strengthen, increase in export is poised to further accelerate economic development, employment and India’s influential position in international trade.
References:
PIB
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1868284
https://static.pib.gov.in/WriteReadData/specificdocs/documents/2025/aug/doc2025814608701.pdf
https://www.pib.gov.in/FactsheetDetails.aspx?Id=149107
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressNoteDetails.aspx?NoteId=154945&ModuleId=3
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressNoteDetails.aspx?id=155151&NoteId=155151&ModuleId=3
Ministry of Textiles
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2156220
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2162261
Ministry of Finance
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2097911
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2108360
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2149736
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2163555
https://gstcouncil.gov.in/sites/default/files/2025-09/press_release_press_information_bureau.pdf
Niti Aayog
https://www.niti.gov.in/sites/default/files/2024-12/Trade-Watch.pdf
World Bank
https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/NE.EXP.GNFS.ZS?locations=IN
https://lpi.worldbank.org/international/global
DD News
https://ddnews.gov.in/en/indias-exports-to-surpass-last-year-despite-tariffs-piyush-goyal/
https://ddnews.gov.in/en/pli-schemes-see-actual-investment-of-rs-1-76-lakh-crore-create-over-12-lakhs-jobs-minister/
https://ddnews.gov.in/en/indias-transformative-decade-landmark-reforms-drive-ease-of-doing-business/
https://ddnews.gov.in/en/india-oman-agree-to-speed-up-talks-on-signing-bilateral-economic-pact/
Twitter
https://x.com/AshwiniVaishnaw/status/1967496528135889375?ref_src=twsrc%5Egoogle%7Ctwcamp%5Eserp%7Ctwgr%5Etweet
Sansad
https://sansad.in/getFile/loksabhaquestions/annex/185/AU2737_MAtnjv.pdf?source=pqals
Niryat.gov.in
https://niryat.gov.in/#?start_date=202404&end_date=202503&sort_table=export_achieved-sort-desc
IBEF
https://www.ibef.org/exports/coffee-industry-in-india
https://www.ibef.org/exports/agriculture-and-food-industry-india
https://ibef.org/news/india-surpasses-china-in-smartphone-exports-to-united-states-us
Invest India
https://www.investindia.gov.in/team-india-blogs/5-key-factors-driving-indias-growth-tech-investment-destination
News on Air
https://www.newsonair.gov.in/new-delhi-hits-out-after-us-announces-additional-tarrifs-asserts-india-will-take-all-necessary-actions-to-protect-national-interests/
https://www.newsonair.gov.in/india-achieves-significant-milestone-in-global-tea-industry-becomes-worlds-2nd-largest-exporter-of-tea-in-2024/
Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation
https://www.mospi.gov.in/sites/default/files/press_release/GDP_PR_Q1_2025-26_29082025.pdf
Ministry of External Affairs
https://www.mea.gov.in/Portal/ForeignRelation/website_brief_India-Hong_Kong_Bilateral_Relations__1_.pdf
https://indbiz.gov.in/dashboard/#ranking
Government of Kerala
https://industry.kerala.gov.in/index.php/district-as-exports-hub
Ministry of Commerce and Industry
https://www.commerce.gov.in/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/LS-Unstarred-No-234.pdf
https://sezindia.gov.in/sites/default/files/factsheet/FACT%20SHEET%20ON%20SEZs%20as%20on%2030.06.2025.pdf
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2156504
https://static.pib.gov.in/WriteReadData/specificdocs/documents/2025/sep/doc2025915637401.pdf
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2101785
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1912572
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2131526
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1907322
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2152518
http://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetailm.aspx?PRID=2108151
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2149736
https://www.investindia.gov.in/team-india-blogs/top-12-indian-sezs-global-investors
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2163475
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2166088
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2160190
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2127826
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2149736
https://indiantradeportal.in/vs.jsp?lang=0&id=0,31,24100,24109
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2168168
Ministry of Electronics & IT
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2147394
Ministry of Ports, Shipping and Waterways
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2112193
Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade
https://www.nsws.gov.in/
CII
https://www.cii.in/International_ResearchPDF/India%20Peru%20Report%202025.pdf
Click here for pdf file
****
SK/M
(Release ID: 2175702)
Visitor Counter : 20749